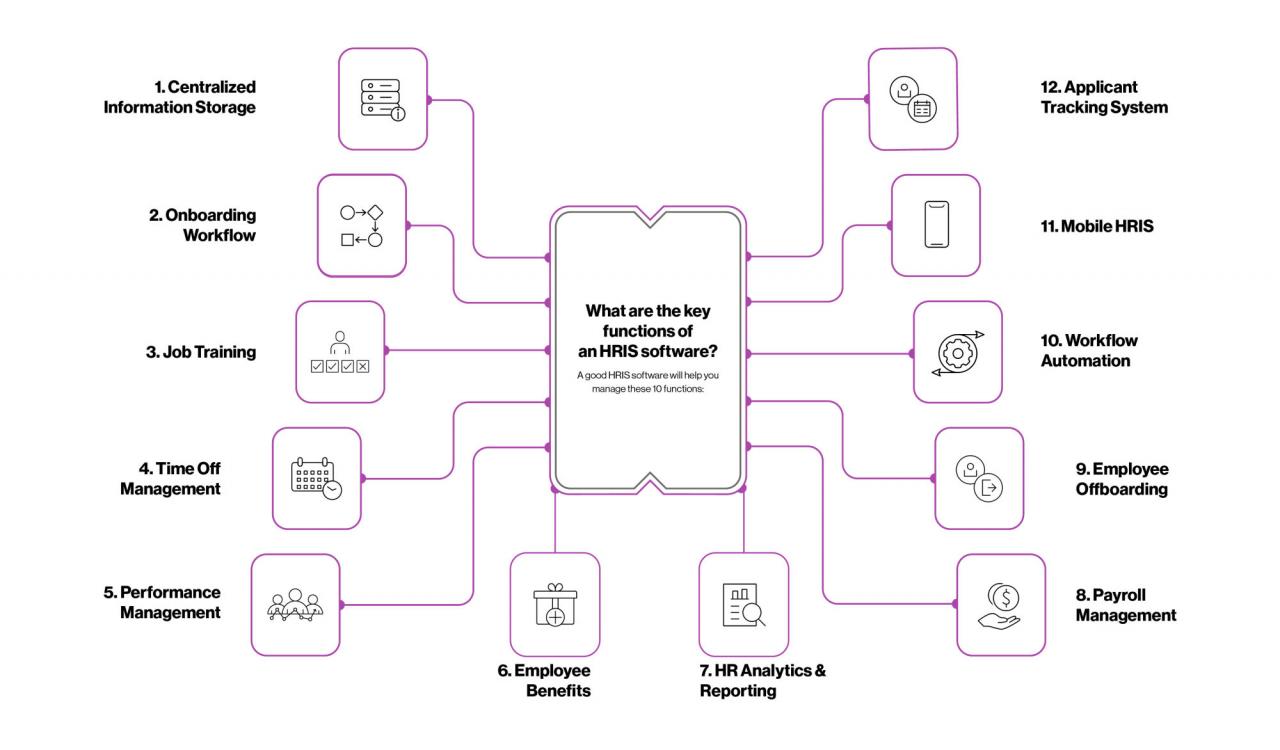
What are the key functionalities of a comprehensive HRIS system? This question is crucial for any business looking to streamline HR processes and boost efficiency. From managing employee data and onboarding to handling payroll and analyzing performance, a robust HRIS system acts as the backbone of modern HR operations. Think of it as a digital command center, consolidating everything from employee records to performance reviews, ultimately empowering HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than getting bogged down in administrative tasks.
A comprehensive HRIS system goes far beyond simple record-keeping. It integrates various HR functions, providing a unified platform for managing the entire employee lifecycle. This includes everything from recruitment and onboarding to performance management, compensation and benefits, and even reporting and analytics. The right system can significantly reduce manual workload, improve data accuracy, and provide valuable insights to drive better HR decisions.
Core HR Management
A robust HRIS system’s core lies in its ability to efficiently manage all aspects of employee lifecycle, from recruitment to retirement. This involves streamlining processes, centralizing data, and providing self-service options that empower both employees and HR professionals. Effective core HR management is the bedrock of a productive and engaged workforce.Employee Self-Service Portals: These portals are designed to empower employees with control over their own HR information and processes.
This not only reduces the administrative burden on HR but also fosters a sense of ownership and autonomy among employees.
Employee Self-Service Portal Features
Employee self-service portals within a comprehensive HRIS system offer a range of functionalities designed to improve efficiency and employee satisfaction. These features typically include access to personal information, benefits enrollment, time-off requests, payroll information, training resources, and performance reviews. The ease of access to these features contributes significantly to a smoother employee experience. For example, an employee can easily update their address, view their payslip, or request vacation time without needing to contact HR directly.
This reduces the workload on HR staff and allows them to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Managing Employee Data
Accurate and readily accessible employee data is crucial for effective HR management. A comprehensive HRIS system provides tools to manage a wide range of employee information, ensuring data integrity and facilitating compliance with various regulations. This includes personal information such as name, date of birth, and address, as well as contact details, emergency contacts, and employment history. Data security and privacy are paramount, and the system should be designed to comply with relevant data protection laws.
Data Entry and Validation Methods
Different methods exist for entering and validating employee data within an HRIS system, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of method often depends on factors such as budget, technical expertise, and the size of the organization.
| Method | Accuracy | Speed | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Data Entry | Moderate (prone to human error) | Slow | Low (initial investment) |
| Automated Data Import (e.g., from spreadsheets) | High (if data is clean) | Fast | Moderate (requires software and expertise) |
| Integration with other systems (e.g., Applicant Tracking System) | High | Fast | High (requires significant integration effort) |
| Optical Character Recognition (OCR) | Moderate (dependent on document quality) | Moderate | Moderate (requires OCR software and potential manual correction) |
Streamlining Onboarding with HRIS
An HRIS system significantly streamlines the onboarding process for new hires, reducing administrative tasks and improving the overall employee experience. Features such as automated offer letters, digital document signing, and integrated background check systems accelerate the process. For instance, an HRIS system can automatically generate personalized onboarding checklists, assign relevant training materials, and track completion status. This ensures a consistent and efficient onboarding experience for all new employees, reducing the time it takes to get them up to speed and contributing to increased employee satisfaction from day one.
Talent Acquisition and Management
A comprehensive HRIS system significantly streamlines the talent acquisition and management process, moving beyond simple applicant tracking to encompass a holistic view of talent from recruitment to performance evaluation. By automating many manual tasks, HR professionals can focus on strategic initiatives and building stronger relationships with candidates and employees. This efficiency translates to cost savings and improved time-to-hire.Applicant tracking and recruitment are core functionalities greatly enhanced by an HRIS.
The system centralizes all aspects of the hiring process, from job posting and applicant screening to interview scheduling and onboarding. This centralized approach minimizes the risk of overlooking qualified candidates and ensures a consistent, fair recruitment process. Features like automated email notifications and applicant tracking dashboards provide real-time insights into the progress of each stage of the hiring pipeline.
Applicant Tracking and Recruitment Features
An HRIS revolutionizes applicant tracking by automating many tedious tasks. Imagine a scenario where a company receives hundreds of applications for a single opening. Manually sorting through resumes and contacting candidates would be incredibly time-consuming. An HRIS automates this process, allowing recruiters to filter applications based on s, skills, and experience. The system can also score applicants based on predefined criteria, helping to prioritize the most promising candidates.
Furthermore, the integrated communication tools allow recruiters to easily send personalized messages to candidates, schedule interviews, and track their progress throughout the hiring process. This ensures a smooth and efficient candidate experience, enhancing the employer brand.
A comprehensive HRIS system boasts functionalities like recruitment, performance management, and employee self-service. But its true power unlocks when you consider seamless data flow, which is why understanding how to effectively integrating HRIS with payroll and other business systems is crucial. This integration streamlines processes and provides a holistic view of your workforce, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of key HR functionalities.
Interview Scheduling Features in HRIS Systems
Different HRIS systems offer varying levels of sophistication in interview scheduling. Some systems provide basic calendar integration, allowing recruiters to manually book interview slots with candidates. Others offer more advanced features, such as automated email reminders, candidate self-scheduling options, and the ability to manage multiple interviewers and interview rounds. For instance, some systems utilize AI-powered scheduling assistants that optimize interview slots based on candidate and interviewer availability, significantly reducing scheduling conflicts and saving time.
High-end systems might even integrate with video conferencing platforms, enabling seamless virtual interviews. The choice of system depends on the organization’s size, complexity, and budget.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Talent Acquisition
Tracking the right KPIs is crucial for measuring the effectiveness of talent acquisition efforts. An HRIS provides the data needed to monitor these metrics and make data-driven decisions.
- Time-to-hire: The time elapsed between posting a job and extending an offer.
- Cost-per-hire: The total cost of recruiting and hiring a new employee.
- Source of hire: Identifying the most effective channels for attracting qualified candidates (e.g., job boards, social media, referrals).
- Applicant-to-interview ratio: The percentage of applicants who are invited for an interview.
- Offer acceptance rate: The percentage of candidates who accept job offers.
- Employee retention rate (within the first year): A measure of how effectively the hiring process identifies suitable candidates who stay with the company.
These metrics help organizations assess the efficiency and effectiveness of their recruitment strategies, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately optimize the talent acquisition process.
Managing Employee Performance Reviews and Feedback with HRIS
An HRIS simplifies performance management by providing a centralized platform for conducting performance reviews, setting goals, and providing feedback. The system can automate the process of scheduling reviews, distributing performance appraisal forms, and collecting feedback from managers and peers. It also allows for tracking employee progress towards goals and identifying areas for development. Furthermore, features like 360-degree feedback capabilities offer a more comprehensive perspective on employee performance.
The data collected can be used to identify top performers, address performance issues proactively, and inform decisions related to compensation, promotions, and training. This structured approach ensures fairness and consistency in performance evaluations and fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Compensation and Benefits Administration

An HRIS system’s effectiveness extends far beyond basic employee data; it plays a crucial role in streamlining compensation and benefits administration, automating processes, and ensuring compliance. This section delves into the intricacies of how HRIS manages payroll and benefits, highlighting the advantages and challenges involved.
A comprehensive HRIS system acts as a central repository for all compensation and benefits data, automating many traditionally manual tasks. This automation not only saves time and reduces administrative overhead but also minimizes errors and ensures accuracy in payroll processing and benefits enrollment. Integration with other systems, such as payroll providers and insurance carriers, further streamlines the process, creating a seamless experience for both HR and employees.
Payroll and Benefits Enrollment Management Methods
HRIS systems employ various methods to manage payroll and benefits enrollment. Payroll processing typically involves integrating with external payroll providers or using built-in payroll modules. This integration allows for the automatic transfer of employee data, such as salary information, deductions, and tax information, directly to the payroll system. Benefits enrollment is often facilitated through self-service portals, allowing employees to access and manage their benefits selections online.
These portals provide real-time updates and allow for easy tracking of benefit usage. Automated workflows can further streamline the process by sending notifications and reminders to employees regarding enrollment deadlines and benefit changes. Many systems offer a variety of options for payment of benefits premiums, such as direct debit or credit card payments.
Benefits Administration Process Flowchart
The following describes a typical benefits administration process within an HRIS system. Imagine a flowchart where each step is a box connected by arrows indicating the flow. Step 1: Open Enrollment Period: The HR department initiates the open enrollment period within the HRIS system. This triggers automated notifications to all eligible employees. Step 2: Employee Access and Selection: Employees access the HRIS self-service portal and review available benefits plans, comparing costs and coverage.
They make their selections and submit their choices electronically. Step 3: Data Validation and Approval: The HRIS system validates the employee’s selections, checking for eligibility and ensuring accurate data entry. This may involve automated checks and manual review by HR personnel. Step 4: System Updates and Communication: Upon approval, the HRIS system updates employee records to reflect their benefit selections. Confirmation messages are automatically sent to employees.
Step 5: Premium Deductions and Payments: The HRIS system automatically calculates premium deductions and integrates with the payroll system to deduct the appropriate amounts from employee paychecks. Step 6: Benefit Administration and Reporting: Throughout the benefit year, the HRIS system tracks benefit usage and generates reports on various aspects of benefits administration, such as cost analysis and utilization rates.
Challenges in Integrating Payroll Data from Different Sources
Integrating payroll data from disparate sources into a unified HRIS system can present several challenges. Inconsistencies in data formats and terminology across different systems are a common hurdle. Data security and compliance concerns also require careful consideration. Ensuring data accuracy and integrity across various systems demands robust data validation and reconciliation processes. Different payroll systems may have varying levels of integration capabilities, leading to compatibility issues.
Finally, the cost and time associated with integration and data migration can be significant. For example, a company with multiple acquisitions might face the challenge of merging payroll data from various acquired companies, each using a different payroll system, into a single, unified HRIS system.
Compensation and Benefit Options Managed within an HRIS
The following table illustrates the various types of compensation and benefits that can be managed within a typical HRIS system.
| Benefit Type | Administration Method | Reporting Capabilities | Integration with other systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Insurance | Online enrollment, premium deduction, claims processing integration | Cost analysis, utilization rates, employee demographics | Payroll, insurance carriers |
| Retirement Plans (401k, Pension) | Contribution tracking, investment options, reporting | Contribution levels, account balances, investment performance | Payroll, financial institutions |
| Paid Time Off (PTO) | Accrual tracking, request management, balance reporting | PTO usage, accrual rates, remaining balances | Payroll, scheduling systems |
| Life Insurance | Enrollment, beneficiary designation, claim processing | Coverage levels, beneficiary information | Insurance carriers |
| Disability Insurance | Enrollment, claim processing | Claim history, benefit payments | Insurance carriers |
| Bonuses and Commissions | Payment processing, performance tracking | Bonus amounts, commission rates, payout history | Payroll, sales management systems |
Reporting and Analytics: What Are The Key Functionalities Of A Comprehensive HRIS System?
A comprehensive HRIS system doesn’t just store employee data; it transforms that data into actionable insights. The reporting and analytics capabilities of a robust HRIS are crucial for strategic decision-making, allowing HR professionals to move beyond reactive problem-solving and into proactive, data-driven strategies. This section explores the power of HRIS data in driving organizational success.Reporting and analytics functionalities provide a deep dive into various aspects of the workforce, offering a holistic view of employee performance, engagement, and overall health.
This data-driven approach empowers HR professionals to make informed decisions, optimize HR processes, and contribute significantly to the company’s bottom line.
Types of Reports Generated by an HRIS
A comprehensive HRIS generates a wide array of reports, catering to various needs within the organization. These reports can be categorized into several key areas, offering detailed insights into various aspects of the workforce. For instance, you might find reports on employee demographics, compensation and benefits analysis, recruitment effectiveness, performance evaluations, training and development progress, and absence and turnover rates.
The specific reports available will depend on the HRIS system’s features and the organization’s specific requirements. Customizable reporting dashboards allow for the creation of tailored reports focusing on key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the business’s strategic goals.
Examples of HR Data Analytics Informing Strategic HR Decisions
HR data analytics goes beyond simple reporting; it uses statistical methods to identify trends, predict future outcomes, and support strategic HR decisions. For example, analyzing employee engagement survey data can reveal areas needing improvement, leading to targeted initiatives to boost morale and productivity. Similarly, analyzing recruitment data can identify bottlenecks in the hiring process, allowing for process optimization and faster time-to-hire.
A comprehensive HRIS system boasts functionalities like payroll processing, recruitment management, and performance tracking. But understanding core functionalities is only half the battle; optimizing the employee experience is key to maximizing HRIS impact. Learn how to leverage your system for better employee engagement by checking out this guide on how to improve employee experience with HRIS.
Ultimately, a well-implemented HRIS streamlines processes and boosts overall employee satisfaction, making it a valuable asset for any organization.
Predictive analytics can even forecast potential attrition risks based on historical data, enabling proactive retention strategies. A company might discover, through analysis of performance reviews coupled with compensation data, that high-performing employees in a specific department are underpaid compared to market rates, prompting adjustments to retain valuable talent.
Tracking Employee Turnover and Identifying Contributing Factors Using HRIS Data
Employee turnover is a costly issue, and HRIS data plays a vital role in understanding its root causes. By tracking metrics like resignation rates, tenure length, and exit interview feedback, HR can identify patterns and potential contributing factors. For example, high turnover in a specific department might point to management issues, while consistently short tenures across the organization could indicate broader problems with compensation or work-life balance.
Analyzing employee feedback from exit interviews, coupled with performance reviews and engagement survey data, provides a comprehensive picture of why employees leave, allowing for targeted interventions to improve retention.
Key HR Metrics, Their Tracking, and Visualizations
Understanding key metrics is essential for effective HR management. The following table showcases some critical metrics, how they are tracked within an HRIS, and the best visualization methods for effective communication and analysis.
| Metric | Tracking Method | Visualization | Example Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Turnover Rate | Tracking employee departures and hires over a period | Line graph showing turnover rate over time | Identify seasonal trends or spikes following specific company events. |
| Average Tenure | Calculating the average length of employment for employees | Bar chart comparing tenure across departments | Highlight departments with unusually short or long tenures. |
| Employee Engagement Score | Analyzing responses from employee surveys | Heatmap showing engagement scores across different teams | Pinpoint teams or departments with low engagement. |
| Time-to-Hire | Tracking time from job posting to offer acceptance | Scatter plot showing time-to-hire vs. job level | Identify bottlenecks in the recruitment process for specific roles. |
Security and Compliance
Protecting employee data is paramount for any HRIS system. A breach can lead to significant legal repercussions, reputational damage, and loss of employee trust. Therefore, robust security measures and adherence to relevant regulations are crucial for a successful and ethical HRIS implementation. This section delves into the critical aspects of security and compliance within a comprehensive HRIS.
A robust HRIS system employs multiple layers of security to safeguard sensitive employee data. This goes beyond simple password protection; it involves a holistic approach encompassing various technical and procedural safeguards. The goal is to minimize vulnerabilities and ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
Data Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption is a fundamental security measure. This involves converting sensitive information into an unreadable format, rendering it useless to unauthorized individuals even if accessed. Access controls, implemented through role-based permissions, ensure that only authorized personnel can access specific data. For instance, a recruiter might have access to applicant information, while a payroll administrator would have access to salary details, but neither would have access to the other’s data.
This granular control minimizes the risk of data breaches and maintains data integrity.
Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
An effective HRIS system must comply with various data privacy regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in California, and other regional or national laws. Compliance involves implementing procedures for data subject access requests, data rectification, and data erasure. Regular audits and assessments ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and legal action.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Data loss can cripple an organization. Therefore, a comprehensive HRIS system includes robust data backup and disaster recovery planning. Regular backups, ideally stored offsite, protect against data loss due to hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. Disaster recovery plans Artikel procedures for restoring data and systems in the event of a major disruption, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
For example, a cloud-based HRIS solution often incorporates automatic backups and geographically redundant data centers to enhance data protection and recovery.
Authentication Methods
Multiple authentication methods enhance security. Beyond basic username and password combinations, multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection. MFA might involve a one-time password (OTP) sent to a mobile device, a biometric scan, or a security token. These methods significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised. Strong password policies, requiring complex passwords and regular changes, further enhance security.
Examples of MFA include using Google Authenticator or similar applications for time-based OTPs, or fingerprint/facial recognition for biometric authentication.
Integration with Other Systems

A truly comprehensive HRIS doesn’t exist in a vacuum. Its power lies in its ability to seamlessly connect with other crucial enterprise systems, creating a unified and efficient flow of information across the organization. This integration fosters better data management, reduces manual data entry, and ultimately, improves decision-making.An HRIS integrates with other systems, such as payroll, accounting, and CRM, through various methods, often involving APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and data synchronization tools.
For instance, employee data changes in the HRIS, like salary adjustments or new hires, are automatically updated in the payroll system, eliminating the need for manual data transfer and minimizing errors. Similarly, data from the HRIS might feed into accounting systems for expense tracking and reporting related to employee compensation and benefits. Integration with a CRM system allows for a holistic view of employee interactions with customers, enabling better performance tracking and targeted training programs.
Data Exchange Methods
Effective integration relies on a well-defined strategy for data exchange. This typically involves real-time synchronization, where data is updated instantly across systems, or batch processing, where data is transferred in scheduled intervals. Choosing the right method depends on factors such as data volume, system capabilities, and the criticality of data accuracy. For example, payroll data usually requires real-time synchronization to ensure timely and accurate payment processing, while less time-sensitive data, such as employee training records, might be handled through batch processing.
The choice also impacts system performance and the complexity of integration processes.
Benefits and Challenges of HRIS Integration
The benefits of integrating an HRIS are substantial, including improved data accuracy, reduced manual work, enhanced efficiency, better decision-making based on consolidated data, and improved employee experience through streamlined processes. However, challenges exist. These include the initial cost of integration, the complexity of managing data across different systems, potential data inconsistencies if not managed properly, and the need for specialized technical expertise to oversee the integration process.
A poorly planned integration can lead to data silos, increased costs due to errors, and a diminished return on investment.
Best Practices for Data Exchange Management, What are the key functionalities of a comprehensive HRIS system?
Successful integration hinges on robust data governance and clearly defined data exchange protocols. This involves establishing data standards, ensuring data quality, and implementing data validation checks to prevent inconsistencies. Regular monitoring and testing of the integrated systems are also crucial to identify and resolve any issues promptly. Prioritizing data security and compliance with relevant regulations is paramount.
A well-defined data mapping process, which Artikels how data fields in different systems correspond, is essential for accurate and reliable data transfer. Furthermore, establishing clear roles and responsibilities for managing the integrated system ensures accountability and effective troubleshooting.
Information Flow Diagram
[Imagine a diagram here. The diagram would show a central HRIS system with arrows pointing to and from other systems like Payroll, Accounting, and CRM. Each arrow would be labeled with the type of data being exchanged, such as “Employee Compensation Data,” “New Hire Information,” or “Employee Performance Metrics.” The diagram would visually represent the interconnectedness and data flow between the HRIS and other crucial enterprise systems, highlighting the circular and interconnected nature of information exchange.
The visual representation would clearly show the central role of the HRIS in facilitating data flow across the organization.]