What are the best HRIS systems for small and medium-sized businesses? This question is top of mind for many entrepreneurs juggling growth and administrative headaches. Finding the right HRIS can be a game-changer, streamlining processes, boosting efficiency, and ultimately freeing up valuable time and resources. But with a plethora of options available, navigating the market can feel overwhelming.
This guide cuts through the noise, helping you pinpoint the perfect HRIS solution to fit your specific needs and budget.
From identifying your core HR requirements—payroll, onboarding, performance management—to understanding the nuances of cloud-based versus on-premise systems, we’ll explore the essential features to consider. We’ll then delve into a comparison of leading HRIS systems, categorized by business size and growth stage, offering insights into pricing models, ease of use, and customer support. Finally, we’ll walk you through the implementation process, highlighting crucial steps for a smooth transition and addressing potential challenges along the way.
Get ready to optimize your HR operations and unlock your business’s full potential!
Defining Needs for Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs): What Are The Best HRIS Systems For Small And Medium-sized Businesses?
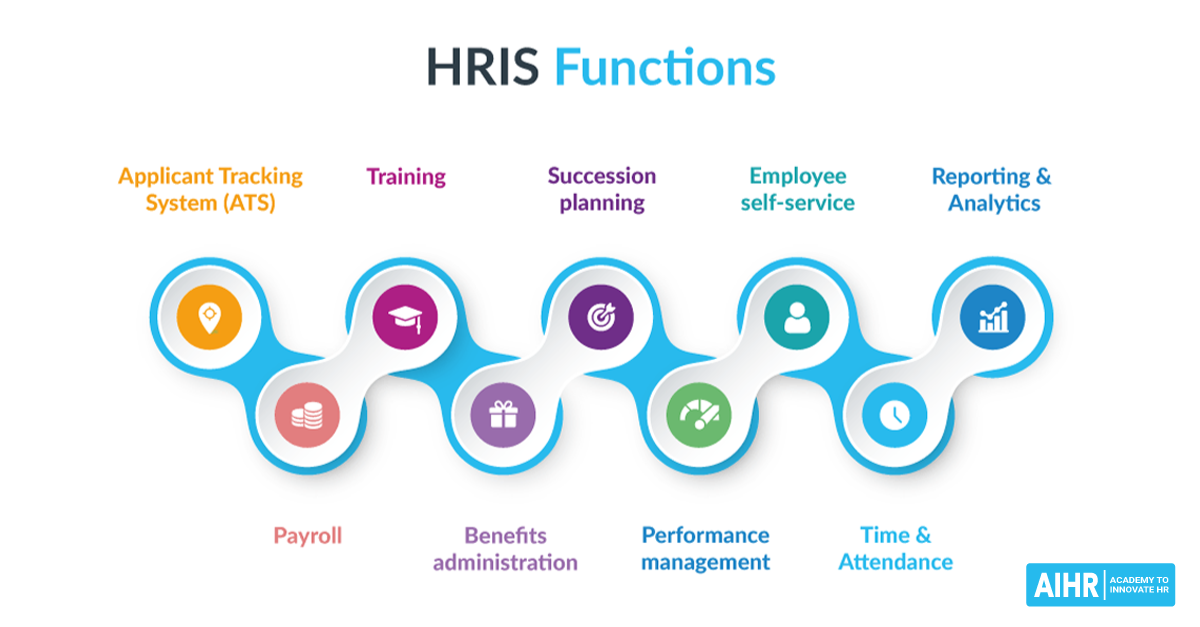
Choosing the right HRIS system hinges on understanding the specific needs of your business. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) face unique challenges, and their HR requirements vary significantly depending on size and growth stage. A system that works flawlessly for a company with 10 employees might be completely inadequate for one with 200.HR functions for SMBs generally encompass core areas like recruitment, onboarding, payroll, benefits administration, performance management, and employee communication.
However, the complexity and sophistication of these functions change dramatically as the company scales.
HR Needs: Small vs. Medium Businesses, What are the best HRIS systems for small and medium-sized businesses?
Small businesses (under 50 employees) often prioritize simplicity and ease of use. They may rely heavily on manual processes for some tasks, and their HR needs are often less complex. The focus is on core functions executed efficiently with minimal administrative overhead. Medium-sized businesses (50-250 employees), on the other hand, require more robust features to manage a larger and more diverse workforce.
They often need advanced reporting capabilities, more sophisticated payroll functions, and more robust compliance features. The need for streamlined workflows and improved efficiency becomes paramount as the workforce grows.
Common Pain Points for SMBs in HR Processes
SMBs frequently grapple with several common HR pain points. Manual data entry is time-consuming and error-prone, leading to inefficiencies and potential compliance issues. Lack of centralized data makes it difficult to track key metrics and make informed decisions. Scattered systems (using different software for payroll, benefits, and other HR functions) lead to integration challenges and data silos.
Finally, the absence of automated workflows slows down processes and increases administrative burden. These challenges can significantly impact productivity and employee satisfaction.
Choosing the best HRIS system for small and medium-sized businesses requires careful consideration of features and budget. For startups especially, finding a cost-effective solution is key, and that’s where exploring options like those highlighted in this guide on cost effective HRIS software for startups becomes crucial. Ultimately, the ideal HRIS will streamline processes and boost efficiency, regardless of company size.
Feature Importance: Small vs. Medium Businesses
The following table highlights the key features that matter most to small versus medium-sized businesses. Note that while some features are important to both, the level of sophistication and complexity required differs significantly.
| Feature | Small Business (Under 50 Employees) | Medium Business (50-250 Employees) |
|---|---|---|
| Payroll Processing | Simple payroll calculation and tax filing; ease of use | Complex payroll calculations, multiple pay schedules, robust tax compliance features, advanced reporting |
| Employee Onboarding | Easy-to-use onboarding portal; basic document management | Automated onboarding workflows, integrated background checks, compliance training modules, performance tracking |
| Time and Attendance Tracking | Basic time tracking capabilities; manual timesheet entry acceptable | Automated time and attendance tracking; integration with payroll; advanced reporting and analytics |
| Reporting and Analytics | Basic reporting on payroll and employee data | Advanced reporting and analytics; customizable dashboards; HR metrics tracking (e.g., turnover, employee satisfaction) |
Exploring Top HRIS System Features

Choosing the right HRIS system is crucial for SMBs to streamline HR processes, boost efficiency, and improve employee satisfaction. A well-chosen system can handle everything from onboarding new hires to managing payroll and tracking employee performance, freeing up valuable time for strategic HR initiatives. Let’s delve into the key features that make an HRIS system truly effective for small and medium-sized businesses.
A robust HRIS system offers a range of functionalities designed to simplify and optimize various HR tasks. The specific needs will vary depending on the size and structure of the business, but certain core features remain consistently important.
Essential HRIS System Features for SMBs
Several features are essential for an HRIS system to effectively serve the needs of an SMB. These features ensure smooth operations, data security, and streamlined processes.
- Employee Self-Service Portal: Allows employees to access information like pay stubs, benefits details, and time-off requests, reducing the administrative burden on HR staff. Imagine the time saved by employees managing their own requests instead of relying solely on HR.
- Recruitment and Onboarding: Streamlines the hiring process from job posting to offer letter generation and onboarding paperwork. This can significantly shorten the time-to-hire and improve the candidate experience.
- Performance Management: Provides tools for setting goals, conducting performance reviews, and tracking employee progress. This allows for more objective evaluations and facilitates employee growth.
- Time and Attendance Tracking: Accurately records employee work hours, simplifying payroll processing and preventing discrepancies. This is crucial for accurate compensation calculations and compliance.
- Payroll Integration: Seamlessly integrates with payroll systems, automating payroll processing and reducing errors. This saves time and ensures accurate and timely payments.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generates reports on various HR metrics, providing valuable insights into workforce trends and employee performance. This data-driven approach allows for informed decision-making.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise HRIS Solutions
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise HRIS solutions significantly impacts cost, scalability, and maintenance. Each option presents advantages and disadvantages that SMBs should carefully consider.
Cloud-based solutions offer accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, automatic updates, and reduced IT infrastructure costs. They are typically more scalable and require less upfront investment. However, reliance on internet connectivity and potential data security concerns are factors to weigh. A small marketing agency, for example, could easily manage its employees’ data and payroll from anywhere using a cloud-based system.
On-premise solutions provide greater control over data security and require no internet connection. However, they involve higher upfront costs for hardware and software, ongoing maintenance expenses, and require dedicated IT support. A manufacturing company with sensitive data might prefer an on-premise solution for heightened security.
HRIS Pricing Models
Understanding the different pricing models is crucial for budgeting effectively. Different vendors offer various pricing structures, each with its own implications.
- Per-user pricing: Charges a fixed fee per employee using the system. This is a straightforward model, easy to understand and budget for. The cost increases linearly with the number of employees.
- Per-module pricing: Charges separately for each module or feature used. This allows for customization, but can lead to higher costs if many modules are needed. A company might choose only the payroll and recruitment modules initially, adding others as needed.
- Tiered pricing: Offers different pricing plans with varying features and user limits. This provides flexibility, allowing businesses to choose a plan that fits their budget and needs. A smaller company might opt for a basic plan, while a larger one chooses a premium plan with more features.
Integration Capabilities with Other Business Software
Seamless integration with other business systems is vital for efficiency and data accuracy. A siloed approach can lead to duplicated data entry, errors, and a lack of holistic insights.
Integration with payroll, accounting, and CRM systems ensures data consistency and eliminates manual data transfer. This streamlines processes and reduces the risk of errors. For instance, integrating the HRIS with the accounting system automates payroll deductions and expense reporting, saving significant time and reducing administrative overhead. Real-time data flow between systems allows for better informed business decisions and improved operational efficiency.
Top HRIS Systems for SMBs

Choosing the right HRIS system is crucial for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). The right system can streamline HR processes, improve employee engagement, and ultimately boost productivity. However, navigating the vast landscape of available options can be overwhelming. This section provides a comparative overview of popular HRIS systems, helping you make an informed decision.
Popular HRIS Systems for SMBs
Several HRIS systems cater specifically to the needs of SMBs, offering a range of features and pricing models. The ideal system will depend on your specific requirements, budget, and future growth plans. The following are some of the most commonly used systems. Note that this is not an exhaustive list, and the suitability of each system varies depending on individual business needs.
| HRIS System | Features | Pricing | Ease of Use | Customer Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BambooHR | Onboarding, payroll, performance management, time tracking, reporting | Starts at around $99/month | Generally considered user-friendly | Good online resources and phone support |
| Zoho People | Recruitment, onboarding, performance management, time off, employee self-service | Offers various plans, starting at a low cost per user | Intuitive interface | Extensive online documentation and customer support |
| Paycor | Payroll, time and attendance, HR management, benefits administration | Pricing varies based on features and employee count | User-friendliness varies depending on the chosen modules | Dedicated support team |
| Gusto | Payroll, benefits administration, compliance tools | Primarily focused on payroll, with additional HR features available | Relatively easy to use for payroll functions | Customer support is generally well-regarded |
| ADP Workforce Now | Comprehensive suite of HR and payroll features | Pricing is tailored to specific needs and business size; usually higher cost | Can have a steeper learning curve compared to other options | Extensive support resources and dedicated account managers |
Categorizing HRIS Systems by Target Market Size
HRIS systems can be broadly categorized based on the size and growth stage of the businesses they best serve. For instance, very small businesses might benefit from simpler, more affordable systems focused on core HR functions. Rapidly growing businesses, however, might need systems with greater scalability and advanced features.
Very Small Businesses (e.g., under 20 employees): Systems like Zoho People or Gusto often provide a good starting point due to their user-friendly interfaces and affordable pricing. These systems offer core HR functionalities without the complexity of larger, enterprise-level solutions. The focus is on ease of use and affordability.
Rapidly Growing Businesses (e.g., 20-200+ employees): Businesses experiencing rapid growth may require systems that can easily scale to accommodate a larger workforce and more complex HR processes. BambooHR, Paycor, and ADP Workforce Now are examples of systems that offer greater scalability and advanced features to manage a growing team effectively. These systems often provide better reporting capabilities and integrate with other business applications.
Evaluating HRIS System Scalability
Evaluating an HRIS system’s scalability is crucial for SMBs anticipating future growth. Consider factors like the system’s ability to handle increasing numbers of employees, its capacity to integrate with other software as your business expands, and the availability of advanced features as your needs evolve. For example, a system with a modular design, allowing you to add features as needed, is generally more scalable than one with a fixed feature set.
A business that starts with 20 employees but anticipates reaching 100 within the next three years should prioritize a system capable of handling that increase in users and data without significant performance issues or the need for a complete system overhaul. This proactive approach ensures that the HRIS remains a valuable asset throughout the company’s growth trajectory, avoiding the disruption and cost of switching systems later.
Choosing the right HRIS system is crucial for SMBs, impacting everything from recruitment to payroll. To stay ahead, understanding the future trends in HRIS technology and automation is key. This knowledge helps businesses select systems that are not only efficient today but also scalable and adaptable to future needs, ensuring long-term HR success for small and medium-sized businesses.
Implementation and Onboarding Considerations

Successfully implementing a new HRIS system is crucial for SMBs to reap its benefits. A well-planned rollout minimizes disruption and ensures a smooth transition for employees and managers alike. Careful consideration of various factors, from data migration to employee training, is essential for a successful outcome.A phased approach is generally recommended, allowing for adjustments and improvements based on initial feedback.
This minimizes the risk of overwhelming the organization with a sudden, large-scale change. Remember, the goal is to improve efficiency and streamline HR processes, not to create more problems.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Implementing a new HRIS system requires a structured approach. Here’s a practical step-by-step guide designed for SMBs:
- Needs Assessment and System Selection: Thoroughly review your existing HR processes and identify areas for improvement. This will guide your selection of an appropriate HRIS system. Consider factors like budget, scalability, and integration capabilities.
- Data Migration Planning: Carefully plan the migration of existing employee data. This often involves cleaning and formatting data to ensure compatibility with the new system. Consider using a third-party data migration specialist for complex data sets.
- System Configuration and Customization: Configure the HRIS system to match your specific business needs and workflows. This might involve customizing reports, workflows, and user permissions.
- Testing and Pilot Program: Conduct thorough testing before a full rollout. A pilot program with a small group of users can identify and resolve potential issues early on. This is crucial to refine processes and identify any training needs.
- Full System Rollout: Once testing is complete, roll out the system to all employees. Schedule this for a time that minimizes disruption to daily operations.
- Post-Implementation Review and Optimization: Regularly review the system’s performance and make necessary adjustments. Gather feedback from employees and managers to identify areas for improvement.
Employee Training and Support
Effective employee training is vital for successful HRIS adoption. Without proper training, employees may resist using the new system, leading to decreased efficiency and frustration.
- Provide comprehensive training materials, including manuals, tutorials, and videos.
- Offer both group and individual training sessions tailored to different roles and skill levels.
- Establish a dedicated support team to address employee queries and concerns.
- Create a user-friendly knowledge base or FAQ document for easy access to information.
- Provide ongoing support and refresher training as needed.
Addressing Implementation Challenges
Data migration and integration issues are common challenges during HRIS implementation. Careful planning and proactive measures can mitigate these risks.Data migration issues can be addressed by employing data cleansing techniques before the migration process. This involves identifying and correcting inconsistencies and errors in the existing data. Integration issues can be resolved by using APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to connect the HRIS system with other business applications, ensuring seamless data flow.
For example, if payroll is handled by a separate system, integrating the two will reduce manual data entry and potential errors.
HRIS Implementation Checklist
A well-defined checklist ensures a smoother implementation process.
- Project Planning: Define project goals, timelines, and budget.
- Vendor Selection: Research and select a suitable HRIS vendor.
- Data Migration: Cleanse and prepare data for migration.
- System Configuration: Customize the system to meet business needs.
- Testing and Pilot Program: Conduct thorough testing before full rollout.
- Employee Training: Develop and deliver comprehensive training materials.
- Go-Live Support: Provide ongoing support to employees.
- Post-Implementation Review: Evaluate the system’s performance and make adjustments.
Security and Data Privacy in HRIS Systems
Choosing the right HRIS system for your small or medium-sized business (SMB) involves more than just finding user-friendly software. Robust security and data privacy features are paramount, especially considering the sensitive nature of employee information stored within these systems. A breach can lead to significant financial losses, legal repercussions, and damage to your company’s reputation. Therefore, understanding the security implications and choosing a system with strong data protection capabilities is crucial.Security features are critical for protecting sensitive employee data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Data privacy compliance, meanwhile, ensures adherence to legal frameworks like GDPR and CCPA, safeguarding your company from hefty fines and legal battles. Implementing strong security measures not only protects your company but also fosters trust and confidence among your employees.
Essential Security Features in HRIS Systems for SMBs
A robust HRIS system should include a multi-layered security approach. This begins with strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires multiple forms of verification to access the system, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized logins. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is essential to protect sensitive information from interception. Regular security audits and penetration testing identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.
Finally, access controls based on the principle of least privilege ensure that employees only have access to the data and functionalities necessary for their roles. Consider systems that offer features like automatic log-out after inactivity periods and IP address restrictions for added protection.
Data Privacy Compliance: GDPR, CCPA, and Beyond
Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in California, is not optional. These regulations mandate specific data handling practices, including obtaining explicit consent for data collection, providing data transparency to employees, and establishing clear procedures for data breaches. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions.
Choosing an HRIS system that is designed with these regulations in mind, and that offers features like data masking and anonymization, simplifies compliance efforts. For example, a system that automatically generates data breach notifications and facilitates data subject access requests will greatly assist with compliance.
Mitigating the Risk of Data Breaches
Proactive measures are crucial in preventing data breaches. Regular software updates patch security vulnerabilities, while employee training programs educate staff on best practices like password security and phishing awareness. Implementing a robust incident response plan Artikels clear steps to take in the event of a breach, minimizing the impact. This includes having a designated point of contact, procedures for containment and investigation, and a communication strategy to inform affected parties.
Consider conducting regular vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses in your system’s security posture.
Managing Employee Access and Permissions
Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) is a fundamental security best practice. RBAC ensures that employees only have access to the information and functionalities relevant to their roles. This minimizes the risk of data breaches caused by unauthorized access. For instance, a receptionist might only need access to employee contact information, while a HR manager would require access to a wider range of sensitive data.
Regularly reviewing and updating employee access permissions is crucial to maintain security as roles and responsibilities change. Detailed audit logs track all access attempts, facilitating the investigation of suspicious activity.