Top HRIS systems with robust analytics and reporting capabilities are revolutionizing HR departments. No longer are HR professionals stuck sifting through endless spreadsheets; instead, they can leverage powerful data visualization tools and insightful reports to make strategic decisions, optimize workforce planning, and improve employee experience. This deep dive explores leading HRIS systems, their analytical strengths, and how they’re transforming the HR landscape.
We’ll examine key features like data visualization, integration capabilities, security protocols, and customization options. We’ll also consider cost-effectiveness and return on investment, along with the crucial aspect of user experience and training. Understanding these elements is vital for choosing the right HRIS system to meet your organization’s unique needs and drive significant improvements in HR efficiency and strategic decision-making.
Defining “Robust Analytics and Reporting” in HRIS
A robust HRIS analytics and reporting system goes beyond basic data collection; it empowers HR professionals with insightful, actionable intelligence to optimize workforce strategies and drive business success. It’s about transforming raw HR data into strategic narratives that inform decision-making across the entire organization.
Key characteristics of robust HR analytics and reporting functionalities include comprehensive data integration, sophisticated data visualization tools, customizable report generation, and the ability to perform predictive analytics. A truly robust system allows for deep dives into specific areas, identifying trends and patterns that might otherwise remain hidden within spreadsheets and disparate databases. This allows for proactive, data-driven decision making, rather than reactive responses to problems.
Top HRIS systems offer invaluable insights through robust analytics and reporting, streamlining HR processes. This is especially crucial for managing remote teams, where the advantages of benefits of cloud-based HRIS systems for remote teams become readily apparent. Ultimately, choosing the right system empowers you to make data-driven decisions, optimizing performance and employee experience, even across geographical boundaries.
Critical HR Metrics
Access to critical HR metrics is paramount for effective strategic HR management. These metrics provide a clear picture of workforce performance, employee engagement, and overall HR effectiveness. The system should easily provide data on key indicators such as employee turnover rates, time-to-hire, cost per hire, employee satisfaction scores, training and development ROI, and diversity and inclusion metrics. Having these readily available allows for quick identification of areas needing attention and facilitates timely interventions.
Report Types Demonstrating Analytical Capabilities
A sophisticated HRIS system offers a variety of report types that showcase its analytical capabilities. Beyond basic headcount reports, a robust system can generate comprehensive reports on workforce demographics, compensation analysis, performance management trends, recruitment effectiveness, and employee engagement levels. Advanced functionalities may include predictive modeling reports forecasting future workforce needs based on historical data and current trends, enabling proactive talent acquisition and succession planning.
Furthermore, customizable dashboards allow users to track key metrics in real-time, providing an always-up-to-date view of the workforce.
Levels of Reporting Sophistication
The level of reporting sophistication directly impacts the depth of insights derived from HR data. Different systems cater to varying needs, offering varying levels of analytical capabilities. The following table illustrates this spectrum:
| Feature | Basic | Intermediate | Advanced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Sources | Limited to core HR data (e.g., payroll, attendance) | Integrates data from multiple sources (e.g., performance management, recruitment) | Integrates with external data sources (e.g., market salary data, economic indicators) |
| Reporting Capabilities | Pre-defined reports (e.g., headcount, turnover) | Customizable reports, basic data visualizations (e.g., charts, graphs) | Advanced analytics, predictive modeling, custom dashboards, real-time data visualization |
| Analysis Techniques | Descriptive statistics (e.g., averages, sums) | Basic statistical analysis (e.g., correlations, trends) | Advanced statistical modeling (e.g., regression analysis, predictive modeling) |
| Data Visualization | Simple tables and lists | Charts and graphs | Interactive dashboards, data storytelling capabilities |
Top HRIS Systems Overview
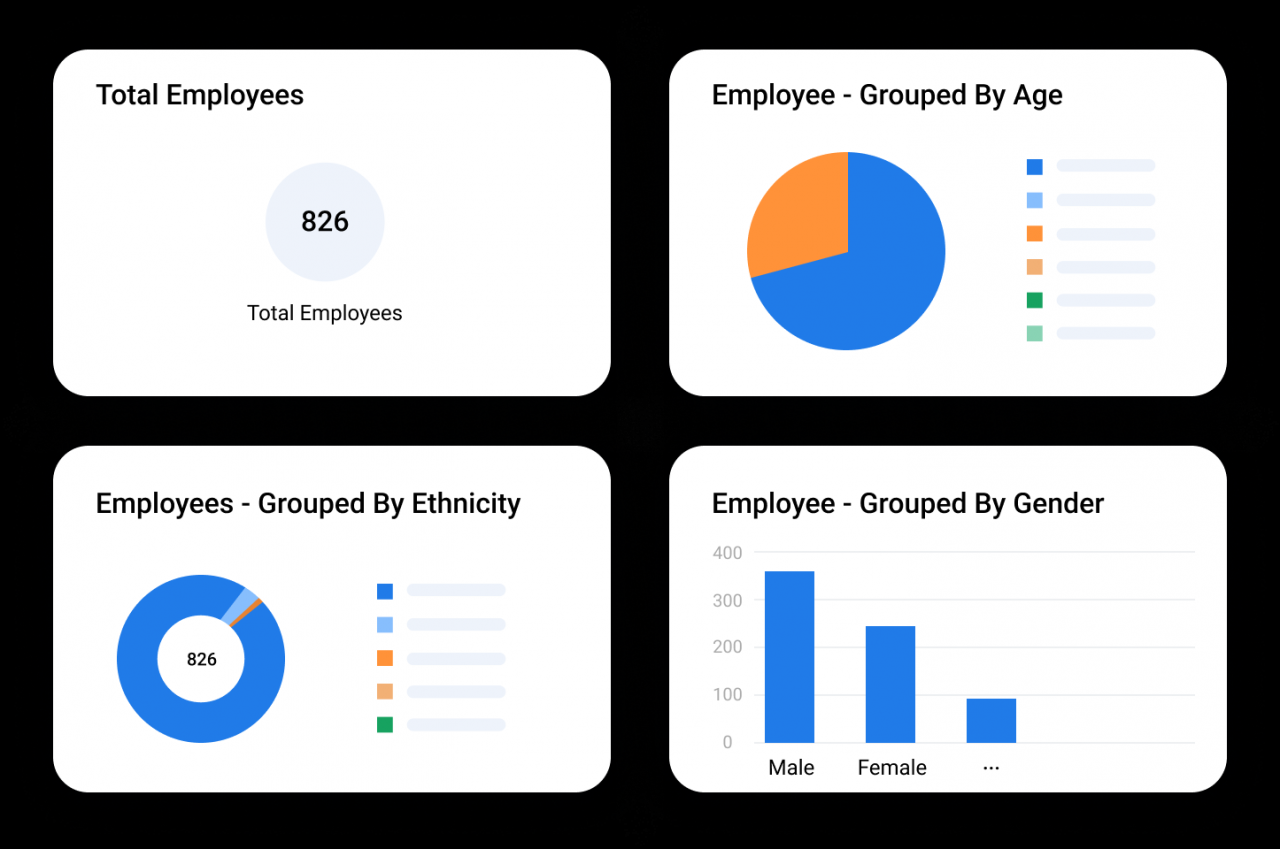
Choosing the right HRIS system is crucial for any organization, especially those prioritizing data-driven decision-making. A robust HRIS system equipped with powerful analytics and reporting capabilities provides invaluable insights into workforce trends, employee performance, and overall HR effectiveness. This section will delve into some leading HRIS systems known for their strong analytical features, highlighting their unique strengths and weaknesses.
Leading HRIS Systems with Robust Analytics
Several HRIS systems stand out for their advanced analytics capabilities. These include industry giants like Workday, Oracle HCM Cloud, and BambooHR, each offering a unique blend of features and functionalities tailored to different organizational needs and sizes. These systems go beyond basic reporting, offering predictive analytics, workforce planning tools, and sophisticated data visualization capabilities. This allows HR professionals to move beyond simply tracking data to actively using it to improve strategic HR initiatives.
Unique Selling Propositions of Three Top-Tier Systems
Workday, Oracle HCM Cloud, and BambooHR each offer distinct advantages. Workday is renowned for its comprehensive suite of integrated HR, payroll, and talent management solutions, all underpinned by a powerful analytics engine. Oracle HCM Cloud boasts a highly customizable platform adaptable to large enterprises with complex HR needs, offering advanced reporting and predictive analytics capabilities. BambooHR, on the other hand, focuses on user-friendliness and ease of implementation, particularly beneficial for smaller businesses, while still providing robust reporting features focused on key HR metrics.
User Interface and Ease of Navigation for Data Analysis
The user interfaces of these systems vary considerably. Workday offers a clean, intuitive interface, with its analytics dashboard providing a clear overview of key metrics. Navigation is generally straightforward, even for users unfamiliar with the system. Oracle HCM Cloud’s interface, while powerful, can feel more complex, requiring a steeper learning curve for effective data analysis. BambooHR prioritizes simplicity, offering a streamlined interface specifically designed for ease of use, making data exploration accessible even to non-technical HR professionals.
The visual representations of data are generally more straightforward in BambooHR compared to the other two, with Workday offering a middle ground.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Selected Systems Regarding Reporting
The following table summarizes the strengths and weaknesses of Workday, Oracle HCM Cloud, and BambooHR concerning reporting capabilities:
| System | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Workday |
|
|
| Oracle HCM Cloud |
|
|
| BambooHR |
|
|
Data Visualization and Presentation Capabilities
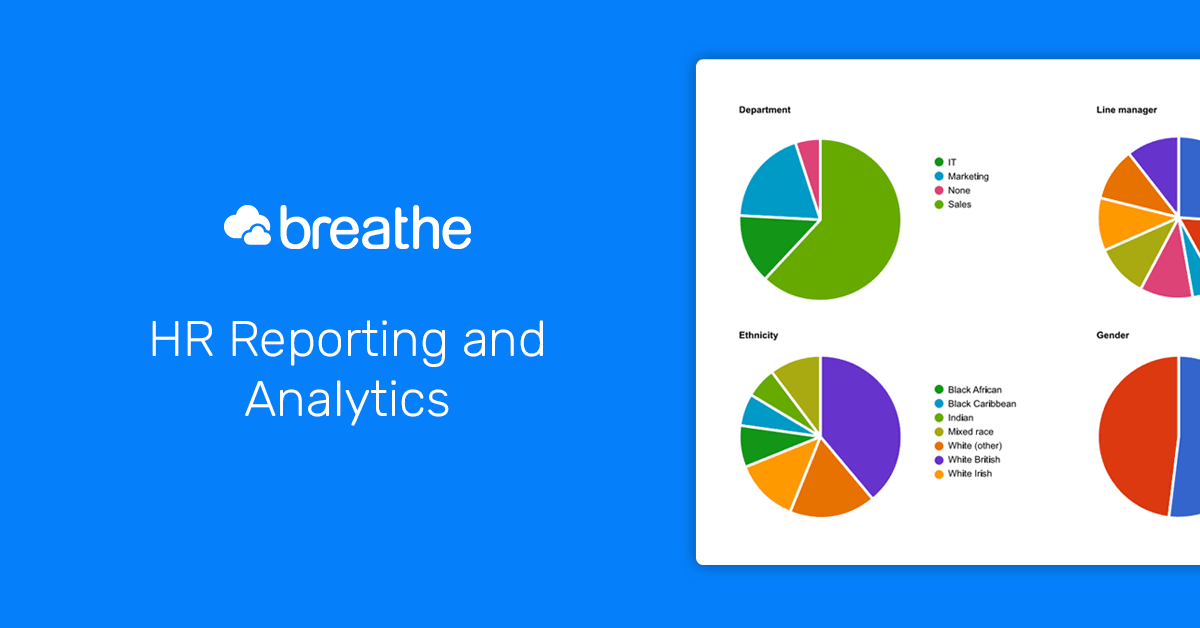
Top HRIS systems go beyond raw data; they offer powerful visualization tools to transform complex information into easily digestible insights. This allows HR professionals to quickly grasp trends, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions that impact the entire organization. Effective data visualization is crucial for translating the wealth of HR data into actionable strategies.Different systems employ a variety of methods to present HR data visually.
Common approaches include bar charts for comparing employee demographics across different departments, pie charts to illustrate the proportion of employees in various job roles, line graphs to track employee turnover rates over time, and scatter plots to explore correlations between variables like employee satisfaction and performance. Many systems also leverage sophisticated dashboards, consolidating multiple visualizations into a single, interactive interface.
Data Visualization in HR Decision-Making
Imagine a scenario where an organization is experiencing high turnover among its entry-level employees. A robust HRIS system, with its data visualization capabilities, could present this issue clearly. A line graph could show a sharp upward trend in turnover rates for this specific employee group over the past year. A bar chart could then compare the turnover rate of entry-level employees with that of other employee groups, highlighting the disparity.
Finally, a scatter plot might reveal a correlation between low salary levels and higher turnover among entry-level employees. This visual representation allows HR to quickly identify the problem and develop targeted solutions, such as salary adjustments or improved onboarding programs, to address the root cause of the high turnover.
Key Features of Effective Data Visualization in HR
Effective data visualization in an HR context prioritizes clarity, accuracy, and relevance. Key features include:
- Clear and Concise Labels: All charts and graphs should have clear titles, axis labels, and legends, ensuring that the data is easily understandable.
- Appropriate Chart Types: The chosen chart type should be suitable for the type of data being presented. For example, a bar chart is best for comparing categories, while a line chart is ideal for showing trends over time.
- Data Accuracy and Integrity: The data presented should be accurate and reliable, reflecting the actual HR data. Any limitations or assumptions should be clearly stated.
- Actionable Insights: The visualizations should not just present data but also highlight key trends and insights that can inform HR decision-making.
- User-Friendly Interface: The visualization tools should be intuitive and easy to use, even for those without extensive data analysis experience.
Interactive Dashboards and HR Data Understanding
Interactive dashboards significantly enhance the understanding of HR data by allowing users to explore information dynamically. For example, an HR manager could use an interactive dashboard to filter employee data by department, location, or job role, and then drill down into specific areas of interest. They could also compare key performance indicators (KPIs) across different groups or time periods, enabling a more comprehensive analysis of HR trends and performance.
Choosing the right HRIS system is crucial, especially those boasting robust analytics and reporting. However, a successful implementation hinges on navigating potential pitfalls; understanding the key challenges is just as important as selecting the right software. For a deep dive into these hurdles and their solutions, check out this comprehensive guide: HRIS system implementation challenges and solutions.
Ultimately, leveraging a top-tier HRIS with strong analytics empowers data-driven decision-making for optimal HR strategies.
The ability to customize views and interact with the data fosters a deeper understanding and empowers more informed decision-making. Imagine a dashboard showing employee satisfaction scores, broken down by department, allowing HR to instantly identify areas needing improvement and target interventions effectively. This real-time, interactive exploration of data is a significant advantage of modern HRIS systems.
Integration and Data Security
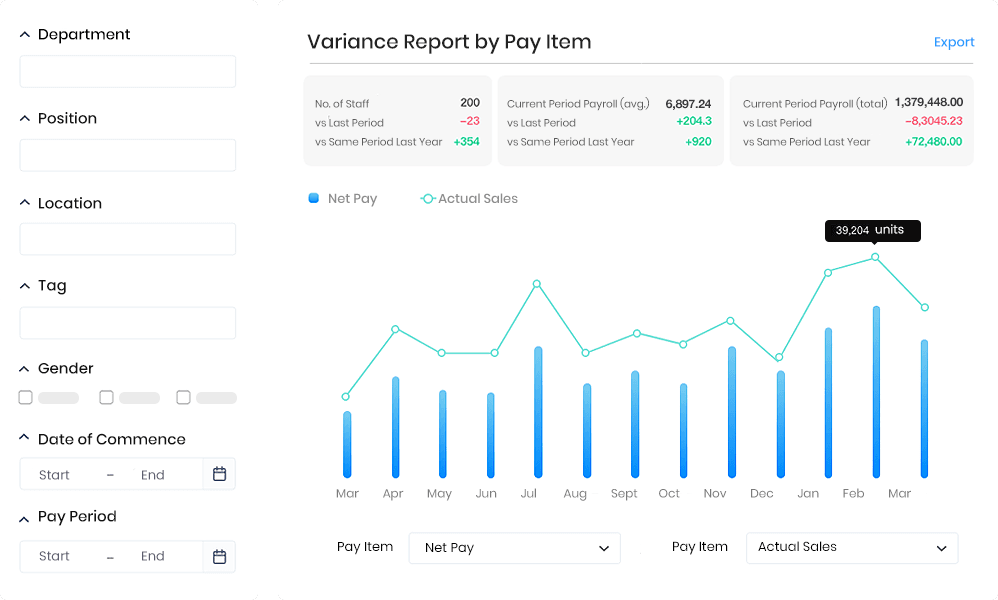
Seamless integration and robust security are paramount for any effective HRIS system. A system that operates in isolation is a liability, while one vulnerable to data breaches risks significant legal and reputational damage. This section explores the critical interplay between integration capabilities and the security measures essential for protecting sensitive employee data.The importance of a well-integrated HRIS cannot be overstated.
Effective integration streamlines workflows, reduces data entry errors, and provides a holistic view of the workforce. By connecting with other business systems like payroll, recruitment platforms, and performance management tools, an HRIS can automate processes, enhance decision-making, and improve overall operational efficiency. Imagine the time saved by automatically updating employee information across multiple systems, eliminating manual data entry and the associated risks of human error.
This integrated approach fosters a more efficient and data-driven HR function.
Seamless Integration with Other Business Systems
Successful HRIS integration hinges on choosing a system with open APIs and robust connectivity options. This allows for the seamless exchange of data with other critical business systems. For example, real-time payroll integration ensures accurate and timely compensation processing, while integrating with recruitment platforms streamlines the hiring process and improves candidate tracking. Furthermore, integrating with performance management tools allows for a holistic view of employee performance, facilitating data-driven decisions on promotions, training, and development.
The key is to select an HRIS that offers flexible integration capabilities, allowing for customization based on the specific needs of the organization.
Security Measures for Protecting Sensitive HR Data
Protecting sensitive employee data is crucial. Robust security measures are essential to prevent unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of HR data. These measures should include multi-factor authentication, data encryption both in transit and at rest, access controls based on the principle of least privilege, regular security audits, and comprehensive employee training programs on data security best practices.
Regular software updates and patching are also vital to address vulnerabilities and protect against known exploits. The system should also comply with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Examples of HRIS Data Breaches and Preventative Measures
Several high-profile data breaches have highlighted the vulnerabilities of HRIS systems. For example, a breach might expose sensitive employee information such as salaries, social security numbers, medical records, and performance reviews. The consequences can be severe, including financial losses, legal liabilities, reputational damage, and loss of employee trust. Preventative measures include implementing strong password policies, regularly backing up data, conducting penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities, and establishing incident response plans to mitigate the impact of a breach.
Employee training on phishing scams and social engineering tactics is also critical.
Data Flow and Security Protocols within a Secure HRIS System, Top HRIS systems with robust analytics and reporting capabilities
The following flowchart illustrates the data flow and security protocols within a secure HRIS system:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with data entry (employee information, performance reviews, etc.), showing the data being encrypted before transmission. It would then depict the data being stored in an encrypted database with access controlled by role-based permissions. Data retrieval would also be shown as encrypted, with audit trails documenting all access attempts.
Finally, it would illustrate the secure deletion or archiving of data when no longer needed, ensuring compliance with data retention policies. The flowchart would visually represent the layers of security involved, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.]
Customization and Scalability
Choosing the right HRIS system hinges not only on its analytical prowess but also on its ability to adapt to your organization’s unique needs and anticipated growth. A truly effective system offers both robust customization options for reporting and the scalability to handle expanding data volumes and user bases. This ensures the system remains a valuable asset as your company evolves.Customizable reporting features allow HR departments to tailor data visualizations and analyses to their specific requirements.
This goes beyond pre-built reports; it involves the ability to create custom reports, dashboards, and alerts based on specific metrics and data points relevant to the organization’s strategic goals. Scalability, on the other hand, ensures the system can handle increased data loads and user numbers without compromising performance or functionality. This is crucial for companies experiencing rapid growth or significant changes in their workforce.
Custom Report Generation and Adaptation to Organizational Needs
The ability to generate custom reports is a cornerstone of a flexible HRIS. Imagine needing to track employee turnover rates specifically within a particular department, or analyzing the effectiveness of a new training program by correlating participation with subsequent performance metrics. A customizable system empowers HR professionals to create these tailored reports, providing actionable insights not available through standard reports.
This level of customization ensures the HRIS remains a relevant and powerful tool, adapting to the ever-changing needs of the organization. For example, a retail company might need to generate reports focusing on employee scheduling efficiency during peak seasons, while a tech firm might prioritize reports on employee skill development and retention. This tailored approach ensures data analysis directly addresses the most critical business challenges.
Scalability and Accommodation of Growing Company Size and Data Volume
Scalability is paramount for long-term HRIS success. As a company grows, so does its data volume. The system must be able to handle this increased load without slowing down or becoming unstable. This includes accommodating a larger number of employees, more complex data structures, and increased user activity. A scalable system can seamlessly integrate new modules or features as the company’s needs evolve, ensuring the HRIS remains a valuable investment throughout its lifecycle.
For instance, a small startup using an HRIS might find it easy to scale up as it grows into a larger enterprise, adding more users, integrating payroll, and expanding reporting capabilities without significant disruption.
Examples of Customizable Reporting Improving HR Efficiency
Several organizations have demonstrated how customized reporting enhances HR efficiency. A large manufacturing company implemented a custom report tracking employee absenteeism by department and shift. This allowed them to identify trends and implement targeted interventions, resulting in a significant reduction in absenteeism costs. Another example involves a global technology company using customized reports to analyze employee satisfaction data, revealing key areas for improvement in employee engagement initiatives.
These targeted improvements led to higher employee retention rates and reduced recruitment costs.
Scalability Comparison of Leading HRIS Vendors
| Vendor | Scalability Model | Data Volume Capacity | User Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor A | Cloud-based, scalable architecture | Highly scalable, adaptable to growing data volumes | Supports thousands of users |
| Vendor B | Hybrid deployment options, modular design | Scalable through add-on modules and cloud integration | Scalable based on chosen deployment and modules |
| Vendor C | On-premise and cloud options, customizable infrastructure | Scalable depending on infrastructure chosen; cloud offers higher scalability | Scalable based on chosen infrastructure; cloud offers higher user capacity |
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI): Top HRIS Systems With Robust Analytics And Reporting Capabilities
Choosing the right HRIS system involves a careful consideration of not just features, but also the financial implications. Understanding the cost structure and potential return on investment is crucial for making a sound business decision. This section explores different pricing models, methods for calculating ROI, and potential cost savings associated with improved HR efficiency.
HRIS Pricing Models
HRIS systems with advanced analytics typically utilize several pricing models. The most common include subscription-based models (often tiered based on the number of employees or features), per-user licensing, and one-time purchase models (less common for systems with ongoing updates and support). Subscription models usually offer greater flexibility, allowing companies to scale their investment as their needs change. Per-user licensing can be cost-effective for smaller organizations, while one-time purchases may offer a lower total cost of ownership over the long term, but often lack ongoing support and updates.
Negotiating contracts is key to securing favorable pricing and ensuring the chosen model aligns with the company’s budget and growth trajectory.
Calculating ROI of HRIS Implementation
Calculating the ROI of an HRIS implementation with robust analytics requires a comprehensive approach. This involves identifying both the costs and benefits associated with the system. Costs include the initial purchase price (or the total cost of the subscription over a defined period), implementation costs (consulting fees, data migration, training), and ongoing maintenance costs. Benefits can include increased HR efficiency (leading to reduced labor costs), improved employee engagement and retention (resulting in lower recruitment and training costs), better data-driven decision-making (leading to more effective HR strategies), and reduced administrative overhead.A simplified ROI calculation can be represented as:
ROI = (Net Benefits – Total Costs) / Total Costs
. For example, consider a company that spends $50,000 on an HRIS implementation. If this leads to a $75,000 reduction in HR administrative costs over three years, the ROI would be ($75,000 – $50,000) / $50,000 = 0.5 or 50%. This calculation, however, is simplified and should ideally include a more detailed breakdown of both costs and benefits over a longer timeframe.
Cost Savings from Improved HR Efficiency
Advanced analytics within an HRIS system can significantly improve HR efficiency. For example, predictive analytics can help identify potential employee turnover risks, allowing HR to proactively intervene and implement retention strategies. This can result in substantial cost savings by reducing recruitment and training expenses. Automated reporting and data analysis can streamline various HR processes, freeing up HR professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Data-driven insights into employee performance can lead to more effective talent management strategies, improving productivity and overall business performance. Consider a company that saves 10 hours per week per HR employee through automation; if the company employs five HR professionals at an average hourly rate of $50, the annual cost savings would amount to approximately $130,000.
Hypothetical Cost-Benefit Analysis
Let’s compare two hypothetical HRIS systems: System A and System B. System A has a one-time purchase price of $75,000 and requires $15,000 in implementation costs. It’s estimated to save the company $30,000 annually in administrative costs and $15,000 annually in reduced turnover costs. System B has a subscription cost of $20,000 annually and requires $10,000 in implementation costs.
It’s estimated to save the company $25,000 annually in administrative costs and $20,000 annually in reduced turnover costs. Over a five-year period, System A would have a total cost of $105,000 and total savings of $225,000, resulting in a net benefit of $120,000. System B would have a total cost of $110,000 and total savings of $225,000, resulting in a net benefit of $115,000.
While System A shows a slightly higher net benefit, the choice depends on the company’s budget constraints and risk tolerance, with System B offering a more predictable and potentially lower upfront cost.