How to choose the right HRIS system for my company? It’s a question plaguing many business owners, a puzzle demanding careful consideration. Finding the perfect HRIS isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about streamlining operations, boosting employee satisfaction, and ultimately, driving business growth. This guide cuts through the jargon, offering a practical roadmap to navigate the complexities of HRIS selection, ensuring you find a system that truly fits your company’s unique needs and aspirations.
From assessing your current HR processes to choosing the right vendor and implementing the system effectively, we’ll cover every crucial step.
Choosing the wrong HRIS can lead to more headaches than solutions. A poorly chosen system might not integrate with your existing software, lack essential features, or simply be too difficult for your employees to use. This can result in wasted time, frustrated employees, and ultimately, a significant drain on resources. This guide helps you avoid those pitfalls by providing a structured approach to choosing the right HRIS, enabling you to make informed decisions and select a system that will truly empower your HR team and your business as a whole.
Assessing Your Company’s Needs: How To Choose The Right HRIS System For My Company
Choosing the right HRIS system is crucial for streamlining HR processes and boosting overall company efficiency. Before you even start browsing software options, a thorough assessment of your company’s specific needs is paramount. This involves understanding your current HR landscape, identifying pain points, and defining your requirements for a new system. Failing to do this properly can lead to selecting a system that doesn’t fully meet your needs, resulting in wasted resources and potential frustration.
Current HR Processes and Pain Points
Understanding your existing HR processes is the first step. This involves mapping out all current HR functions, from recruitment and onboarding to performance management and payroll. Identify bottlenecks and areas where processes are inefficient or time-consuming. For example, are you spending excessive time on manual data entry? Are reports difficult to generate?
Are communication processes with employees cumbersome? Pinpointing these pain points will help you prioritize features in your new HRIS system. A clear picture of these inefficiencies will allow you to accurately assess how an HRIS can provide a solution. For instance, a company struggling with manual payroll processing could benefit significantly from an HRIS with automated payroll capabilities.
Choosing the right HRIS system involves careful consideration of your company’s size, budget, and specific needs. For startups navigating early growth, finding a cost-effective solution is key, and that’s where exploring options like those highlighted in this guide on cost effective HRIS software for startups can be incredibly beneficial. Ultimately, the best HRIS system will streamline your processes, improve efficiency, and support your company’s overall growth trajectory.
Must-Have HRIS Features
Once you’ve identified your pain points, you can create a prioritized list of must-have features for your HRIS. This list should be tailored to your company’s size, industry, and employee count. The importance of each feature should be clearly defined.
| Feature | Importance | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Employee Self-Service Portal | High | Empowers employees to manage their own information (e.g., time-off requests, personal details), reducing HR workload and improving employee satisfaction. This is especially important for larger companies with numerous employees. |
| Payroll Integration | High | Automates payroll processing, reducing errors and saving time. Essential for all companies, but particularly crucial for those with large payrolls or complex compensation structures. |
| Recruitment and Onboarding Modules | Medium | Streamlines the hiring process, from job postings to offer letters and onboarding paperwork. More critical for companies with high employee turnover or frequent hiring needs. |
| Performance Management Tools | Medium | Facilitates performance reviews, goal setting, and employee development. Important for companies focused on employee growth and performance improvement. |
| Reporting and Analytics | High | Provides valuable data-driven insights into HR metrics, enabling better decision-making. Essential for all companies to track key HR indicators. |
| Time and Attendance Tracking | Medium | Automates time tracking and simplifies payroll calculations. More critical for companies with hourly employees or complex scheduling requirements. |
Budget and Implementation Timeline
Establishing a clear budget and implementation timeline is crucial for a successful HRIS deployment. Consider factors such as software licensing fees, implementation costs (consulting, training, data migration), and ongoing maintenance expenses. A realistic timeline should be developed, taking into account the complexity of the system and the integration with existing systems. For example, a small company might allocate a budget of $5,000-$10,000 and a timeline of 3-6 months, while a larger enterprise might require a significantly larger budget and a longer implementation period.
Integration Requirements
Many companies already have existing systems in place, such as payroll software or accounting systems. Therefore, assessing the need for integration with these systems is critical. This involves identifying which systems need to be connected to the HRIS and determining the level of integration required. Seamless integration can significantly improve data accuracy and reduce manual data entry.
For example, integrating the HRIS with the payroll system can automate the transfer of employee data, reducing the risk of errors and saving time. A successful integration plan should consider data migration strategies, data security protocols, and testing procedures.
Researching and Comparing HRIS Vendors
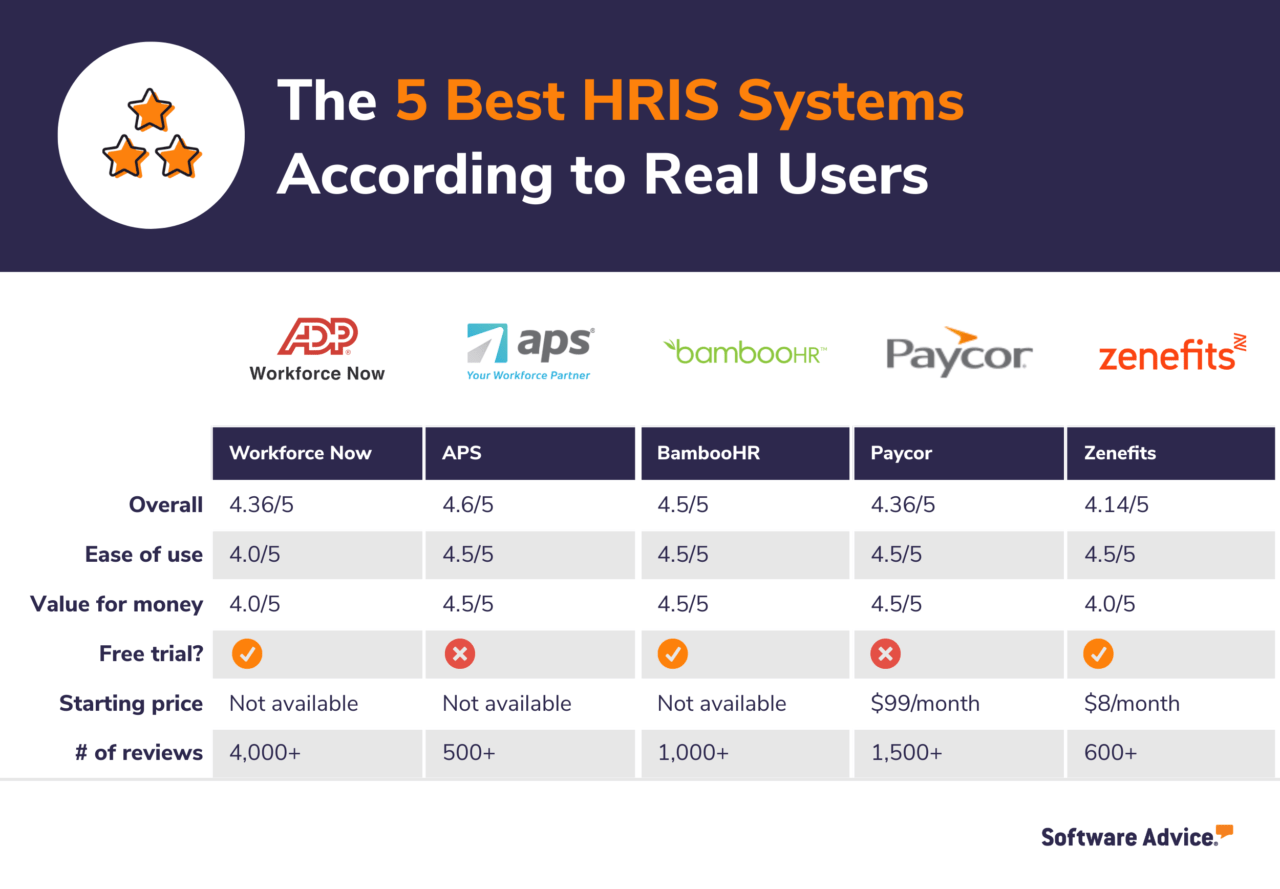
Choosing the right HRIS system is a crucial decision, impacting efficiency, employee satisfaction, and overall business success. Thorough research and vendor comparison are essential to avoid costly mistakes and ensure a smooth implementation. This involves understanding different vendors’ offerings, their pricing structures, and the level of support they provide.
HRIS Vendor Comparison
Selecting the ideal HRIS often involves weighing various options. To illustrate, let’s compare three popular vendors: BambooHR, Gusto, and Workday. This comparison focuses on key features relevant to many businesses, but remember that specific needs will dictate the best choice for your company.
| Feature | BambooHR | Gusto | Workday |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Features | Onboarding, performance management, time off tracking, employee directory. | Payroll, benefits administration, hiring tools, time tracking. | Comprehensive suite including talent management, payroll, benefits, recruiting, and analytics. |
| Pricing Model | Per-employee, monthly subscription. | Per-employee, monthly subscription, with additional fees for certain features. | Enterprise-level pricing, typically negotiated based on company size and needs. |
| Customer Support | Phone, email, and online resources. | Phone, email, and online help center. | Dedicated account manager and extensive online support resources. |
Deployment Models: Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise
Companies must decide between cloud-based and on-premise deployment models. Cloud-based systems, like those offered by BambooHR and Gusto, are hosted by the vendor, offering accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. On-premise systems, often associated with larger, more complex solutions like Workday, require the company to host the software on its own servers.Cloud-based deployment offers advantages such as lower upfront costs, easier maintenance, and scalability.
However, it relies on a stable internet connection and data security depends on the vendor. On-premise solutions provide greater control over data and security but demand significant upfront investment in hardware and IT infrastructure, along with ongoing maintenance responsibilities. The choice depends on your company’s IT capabilities, budget, and security requirements. A small business might favor the ease and affordability of a cloud-based system, while a large corporation with stringent security needs might opt for on-premise.
Vendor Reputation, Security, and Scalability
Before committing to a vendor, investigate their reputation through online reviews and industry reports. Security measures are paramount; ensure the vendor complies with relevant data privacy regulations (like GDPR or CCPA) and employs robust security protocols. Scalability is also critical – the system should be able to adapt to your company’s growth, accommodating increasing numbers of employees and data without significant performance issues.
Consider future expansion plans when making your decision. A system that struggles to handle growth can quickly become a bottleneck.
Evaluating System Features and Functionality
Choosing the right HRIS system isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about ensuring the software seamlessly integrates with your company’s unique needs and workflows. A robust HRIS system should streamline processes, improve efficiency, and empower your HR team to make data-driven decisions. This involves a careful evaluation of its core features and functionality, ensuring they align perfectly with your current and future operational requirements.
The key to successful HRIS implementation lies in understanding what your business needs from the system and ensuring that the selected vendor can deliver on those expectations. A poorly chosen system can lead to frustration, decreased productivity, and ultimately, a negative impact on your bottom line.
Core HR Functions Supported by the System
A comprehensive HRIS system should handle a wide range of essential HR functions. The specific needs will vary based on company size and complexity, but the following represent core functionalities to consider:
- Payroll: Automated payroll processing, tax calculations, direct deposit, and reporting capabilities are crucial for accurate and timely compensation distribution. Consider features like integration with existing accounting software for seamless data transfer.
- Benefits Administration: Efficient management of employee benefits, including enrollment, tracking, and communication regarding health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. Look for systems that allow for self-service employee access and automated reporting for compliance.
- Recruitment: Streamlining the recruitment process from job posting and applicant tracking to interview scheduling and onboarding. Features like applicant screening tools, automated communication, and integration with job boards are highly valuable.
- Performance Management: Facilitating performance reviews, goal setting, and employee development. A good system will offer features for goal tracking, feedback mechanisms, and performance data analysis to support informed decisions.
- Time and Attendance: Accurate tracking of employee work hours, including overtime, vacation, and sick leave. Integration with payroll is essential for accurate compensation calculations and reporting.
- Learning and Development: Managing training programs, tracking employee progress, and assessing the effectiveness of learning initiatives. Features like course catalogs, online learning platforms, and progress tracking are key.
User-Friendliness and Employee Adoption
Even the most feature-rich HRIS system will fail if employees refuse to use it. A poorly designed interface can lead to frustration, errors, and ultimately, low adoption rates. Prioritize systems with intuitive navigation, clear layouts, and user-friendly features. Consider factors like mobile accessibility and the overall user experience. A system that’s difficult to navigate will likely result in wasted time and decreased productivity, undermining the very purpose of implementing the HRIS in the first place.
Choosing the right HRIS system is crucial for boosting productivity and employee satisfaction. A key factor to consider is how well the system supports employee engagement; to help you, check out this insightful guide on comparing top HRIS systems for employee engagement. Ultimately, selecting the right HRIS boils down to aligning its features with your company’s specific needs and goals for a more engaged workforce.
For example, a system with a clunky interface might lead employees to revert to manual processes, negating the efficiency gains promised by the technology.
Reporting and Analytics Capabilities
Beyond basic HR functions, a strong HRIS system provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities. This data-driven approach allows HR professionals to gain valuable insights into workforce trends, employee performance, and overall organizational effectiveness. Effective reporting and analytics are essential for informed strategic decision-making. For instance, analyzing employee turnover rates can highlight potential issues with compensation, benefits, or work-life balance, enabling proactive interventions.
Consider the types of reports the system generates (e.g., workforce demographics, performance metrics, compensation analysis) and the ability to customize reports to meet specific needs. Data visualization tools, dashboards, and the ability to export data to other applications are also critical features to consider. A system that can provide clear, concise visualizations of key HR metrics allows for quicker identification of trends and better strategic planning.
Implementation and Integration
Successfully choosing an HRIS system is only half the battle. A smooth implementation and seamless integration with existing systems are crucial for maximizing ROI and minimizing disruption to your daily operations. This phase requires meticulous planning and execution to ensure a positive user experience and a swift transition.Implementing a new HRIS system involves a multifaceted approach, demanding careful consideration of data migration, user training, and rigorous system testing.
Effective integration with existing business applications, such as payroll and accounting software, is also paramount for streamlining workflows and avoiding data silos. Let’s delve into the key steps involved.
Data Migration Strategies
Migrating data from your old system to the new HRIS is a critical step. A poorly executed migration can lead to data loss, inaccuracies, and significant delays. Consider a phased approach, starting with a pilot migration of a small subset of data to test the process and identify potential issues before tackling the entire database. This allows for adjustments and refinements to ensure a clean and accurate transfer of employee information, compensation details, performance reviews, and other crucial data points.
Regular backups throughout the migration process are essential to safeguard against unforeseen problems. Employing data cleansing techniques before migration is crucial to eliminate inconsistencies and inaccuracies in the existing data. For instance, standardizing date formats and employee identification numbers will prevent errors during the transfer.
User Training and Support, How to choose the right HRIS system for my company
Comprehensive user training is paramount for successful HRIS adoption. A well-designed training program should cover all aspects of the new system, from basic navigation to advanced features. This could involve online modules, instructor-led sessions, or a blended approach. Consider providing different training levels catering to various roles and skill sets within the HR department and across the organization.
Ongoing support through FAQs, help desk assistance, and readily available documentation is equally important to address any questions or issues users might encounter after the initial training. For example, providing quick reference guides or short video tutorials can be incredibly helpful for users to quickly access information on specific functionalities.
System Testing and Quality Assurance
Thorough testing is essential to ensure the new HRIS functions correctly and meets the company’s needs. This should include unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT). Unit testing verifies individual components, integration testing ensures different parts work together seamlessly, and UAT involves end-users testing the system to identify any usability issues or functional gaps. Testing should be conducted in a controlled environment before the full rollout to minimize disruption to live operations.
Documentation of testing results, including any bugs or issues identified, is vital for tracking progress and addressing any outstanding problems. For example, a detailed bug report with screenshots and step-by-step instructions for reproducing the error can be invaluable for developers.
Integration with Other Business Applications
Integrating the HRIS with other business applications, like payroll and accounting software, is crucial for streamlining workflows and preventing data duplication. This often involves using APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to enable data exchange between systems. Before initiating integration, carefully assess the compatibility of the different systems and choose integration methods appropriate for your specific needs. For example, real-time integration ensures data is always synchronized, while batch processing might be sufficient for less time-sensitive data.
Regularly review and update integrations to accommodate changes in either system to maintain a smooth data flow. Consider a phased integration approach, starting with critical systems and gradually expanding to others.
Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Choosing the right HRIS system is only half the battle. The ongoing support and maintenance you receive from your vendor are crucial for the system’s long-term success and your company’s overall HR efficiency. Neglecting this aspect can lead to costly downtime, data breaches, and a frustrated HR team. Investing in a robust support package is an investment in your company’s future.A comprehensive support and maintenance contract typically includes various levels of assistance, ensuring your HRIS remains functional, secure, and up-to-date.
This ranges from basic troubleshooting and technical assistance to proactive maintenance and system upgrades. The level of support offered will vary depending on the vendor and the specific contract you choose, but understanding these options is critical for making an informed decision.
Types of Support Offered
Vendors usually offer tiered support packages, ranging from basic phone and email support to premium options including dedicated account managers and priority response times. Basic packages often cover troubleshooting common issues, while premium packages may include proactive system monitoring, preventative maintenance, and rapid response to critical incidents. Some vendors even offer 24/7 support, crucial for companies operating globally or with around-the-clock operations.
Consider the size of your company and your tolerance for downtime when selecting a support level. For example, a large multinational corporation might benefit from a premium 24/7 support package, while a smaller company might find a basic package sufficient.
Addressing Post-Implementation Issues
Even with careful planning, issues can arise after your HRIS implementation. These could range from minor glitches in reporting to more significant problems such as data corruption or integration failures. Effective vendor support is vital in addressing these promptly. For instance, imagine a scenario where a critical payroll update fails due to a software bug. A responsive vendor with a strong support system can quickly diagnose the problem, implement a fix, and minimize disruption to your payroll process.
Without this, the consequences could be severe, impacting employee morale and potentially leading to legal complications. Another example could be a sudden surge in user support requests due to a poorly understood system update. A vendor with proactive communication and comprehensive documentation can mitigate this by providing timely training and support materials.
Ongoing System Administration and Maintenance Checklist
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring your HRIS operates smoothly and securely. This involves a combination of tasks performed by your internal team and your vendor. A proactive approach can prevent small issues from escalating into larger, more costly problems.
- Regular software updates and patches
- Data backups and disaster recovery planning
- Security audits and vulnerability assessments
- User access management and role-based permissions
- Performance monitoring and optimization
- Regular system testing and validation
- Proactive communication with the vendor regarding any issues or concerns
- Training for new users and updates for existing users
- Documentation of system processes and configurations
- Review and update of HR policies and procedures to align with the system