Best practices for HRIS data management and reporting are crucial for any organization aiming for efficiency and strategic decision-making. This isn’t just about storing employee information; it’s about leveraging that data to drive improvements in recruitment, retention, compensation, and overall HR effectiveness. We’ll delve into the key aspects, from ensuring data security and integrity to harnessing the power of data visualization for insightful reporting.
From data governance and security to insightful reporting and analytics, mastering HRIS data management is key to unlocking the true potential of your HR function. This involves implementing robust security measures, ensuring data accuracy through cleansing and validation, and leveraging advanced analytics to make informed decisions. Think of it as transforming raw employee data into actionable intelligence that fuels your organization’s growth.
Data Governance and Security: Best Practices For HRIS Data Management And Reporting
Maintaining the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of HRIS data is paramount for any organization. A robust data governance framework and stringent security measures are crucial not only for compliance but also for fostering trust among employees and protecting the organization’s reputation. Neglecting these aspects can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions, as well as damage to employee morale.
Mastering best practices for HRIS data management and reporting is crucial for any business, ensuring accurate insights for strategic decision-making. Finding the right HRIS system is key to this process, and for startups, choosing a cost-effective solution is paramount. That’s why exploring options like cost effective HRIS software for startups can significantly improve your data handling capabilities.
Ultimately, efficient data management, enabled by the right software, leads to better reporting and informed HR strategies.
Effective HRIS data governance requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing data quality, access control, and compliance with relevant regulations. This involves defining clear roles and responsibilities, establishing data ownership, and implementing processes for data validation and verification. Furthermore, regular audits and reviews are necessary to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of the governance framework and to identify areas for improvement.
HRIS Data Governance Framework Elements
A robust HRIS data governance framework includes several key elements. These elements work together to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and security. Defining clear data ownership and establishing data quality standards are foundational. Regular data audits and a well-defined process for handling data breaches are also critical components. Finally, comprehensive documentation of all data governance policies and procedures is essential for transparency and accountability.
This ensures everyone understands their responsibilities and how to adhere to established guidelines.
Securing HRIS Data
Securing HRIS data necessitates a multi-layered approach combining technical and administrative controls. Encryption, both in transit and at rest, is a crucial element for protecting sensitive employee information. Strong access control measures, including role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), limit access to authorized personnel only. Regular security assessments and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities and strengthen the system’s defenses against potential threats.
Employee training on data security best practices is also essential to prevent human error, a major cause of data breaches.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Policies
Comprehensive data backup and disaster recovery plans are vital for ensuring business continuity in the event of a system failure, natural disaster, or cyberattack. These plans should detail the frequency of backups, the location of backup storage (on-site and off-site), and the procedures for restoring data. Regular testing of the disaster recovery plan is essential to ensure its effectiveness and to identify any gaps or weaknesses.
The plan should also include procedures for notifying employees and other stakeholders in the event of a disruption. Consideration should be given to the recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO) to define acceptable downtime and data loss. For example, a plan might specify a RTO of 4 hours and an RPO of 24 hours.
Data Encryption Methods Comparison
| Method | Security Level | Implementation Complexity | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) | High | Medium | Medium |
| RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) | High | High | High |
| 3DES (Triple DES) | Medium | Medium | Low |
| PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) | High | Medium | Medium |
Data Integration and Migration
Seamlessly integrating your HRIS data with other crucial enterprise systems and migrating data to a new system are pivotal for maintaining accurate, accessible, and actionable HR information. Effective strategies and meticulous planning are essential to avoid costly errors and disruptions. This section details best practices to ensure a smooth and efficient process.Data integration and migration are complex processes requiring careful planning and execution.
A poorly executed migration can lead to data loss, inaccuracies, and significant operational disruptions. Conversely, a well-planned migration can streamline HR processes, improve data quality, and enhance decision-making.
Integrating HRIS Data with Other Enterprise Systems
Successful integration of HRIS data with other systems like payroll and benefits requires a well-defined strategy. This involves choosing the right integration method (e.g., real-time, batch processing), establishing clear data mapping rules, and implementing robust error handling mechanisms. For instance, real-time integration ensures data consistency across systems, while batch processing may be more suitable for less time-sensitive data.
Thorough testing and validation are crucial to verify data accuracy and integrity after integration. A key consideration is the security of data transfer between systems, requiring secure protocols and access controls.
Steps Involved in Migrating HRIS Data to a New System
Migrating HRIS data involves several key steps. First, a thorough assessment of the current system and data quality is needed. This involves identifying data inconsistencies, duplicates, and missing values. Next, a detailed migration plan should be created, outlining the timeline, resources, and responsibilities. Data cleansing and transformation are crucial to ensure data accuracy and consistency before migration.
The actual data migration process involves transferring data from the old system to the new system, often using specialized tools. Finally, post-migration validation is essential to verify data integrity and accuracy in the new system. This often involves comparing data in both systems and resolving any discrepancies.
Checklist for Successful HRIS Data Migration
A comprehensive checklist is vital for a successful migration. Pre-migration activities include: defining project scope and objectives, selecting migration tools, and performing a thorough data assessment. During migration, activities include: data cleansing, transformation, and loading into the new system. Post-migration activities include: data validation, user acceptance testing, and system stabilization. Each stage should have defined success criteria and contingency plans.
For example, a pre-migration data quality assessment might involve running reports to identify duplicate employee records or inconsistencies in data fields.
Handling Data Inconsistencies During Migration
Data inconsistencies are inevitable during migration. Strategies for handling these include: establishing clear data quality rules and standards, using data cleansing tools to identify and correct inconsistencies, and developing procedures for handling exceptions. For example, if an employee’s date of birth is inconsistent across different systems, a standardized process should be in place to determine the correct value.
This might involve referencing original documentation or contacting the employee directly. Documentation of all decisions and changes made is critical for audit trails and future reference.
Data Quality and Cleansing

Maintaining high-quality data within your HRIS is crucial for accurate reporting, effective decision-making, and compliance. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to significant problems, from flawed performance reviews to incorrect payroll calculations. This section details common data quality issues, methods for identifying and correcting them, and a step-by-step process for data cleansing.Data quality issues in HRIS systems often stem from manual data entry errors, inconsistent data formats, and a lack of standardized processes.
These issues can manifest in various ways, leading to inaccurate reporting, flawed analytics, and potentially costly legal issues. For example, incorrect employee contact information can hinder communication during emergencies, while inconsistent job title entries make workforce planning challenging. Inaccurate compensation data can lead to payroll errors and legal disputes.
Common Data Quality Issues and Their Impact
Inaccurate, incomplete, and inconsistent data are the most prevalent issues. Inaccurate data leads to flawed reports and analyses, impacting strategic decisions. Incomplete data hinders comprehensive reporting and analysis, creating gaps in information. Inconsistent data, such as variations in date formats or job titles, complicates data analysis and reporting, making it difficult to draw accurate conclusions. These issues can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
For instance, incorrect tax information could result in substantial penalties.
Methods for Identifying and Correcting Inaccurate Data
Identifying and correcting inaccurate data requires a multi-pronged approach. Data profiling helps to understand the characteristics of the data, revealing inconsistencies and anomalies. This involves analyzing data for patterns, identifying outliers, and assessing data completeness. Data validation rules, such as checking for valid date formats or ensuring that salary figures are within a reasonable range, help to prevent inaccurate data from entering the system in the first place.
Regular data audits and reconciliation against other systems, like payroll or benefits providers, further help to identify and correct inaccuracies. Manual review, especially for complex or sensitive data, is also often necessary. For example, comparing data from the HRIS to official government identification documents can verify employee information.
Data Validation Rules for Ensuring Data Accuracy
Data validation rules are essential for maintaining data accuracy. These rules act as checks and balances, ensuring data conforms to predefined standards before being accepted into the system. Examples include: checking for valid email addresses, enforcing specific date formats (e.g., YYYY-MM-DD), validating numerical ranges (e.g., ensuring age is within a realistic range), and using drop-down lists for standardized values like job titles or departments.
These rules should be designed based on the specific requirements of each data field and enforced throughout the data entry and update processes. For example, a rule could prevent the entry of a salary exceeding a pre-defined maximum for a specific job grade.
Step-by-Step Process for Data Cleansing
Data cleansing is an iterative process that requires careful planning and execution.
- Data Profiling: Analyze the data to identify patterns, inconsistencies, and anomalies. This involves using data profiling tools to generate descriptive statistics and identify data quality issues.
- Standardization: Convert data into a consistent format. This includes standardizing date formats, addresses, and other data fields to ensure uniformity across the dataset. For example, converting all date formats to YYYY-MM-DD.
- Deduplication: Identify and remove duplicate records. This involves comparing records based on key fields like employee ID or social security number to eliminate redundant entries. Sophisticated matching algorithms can be employed to identify near-duplicates based on fuzzy matching techniques.
- Data Correction: Correct identified inaccuracies. This might involve manual review and correction of individual records, or the use of automated tools to correct common errors.
- Data Validation: Re-validate the cleansed data to ensure accuracy and completeness. This involves running data validation rules to identify any remaining errors and ensure the data meets predefined quality standards.
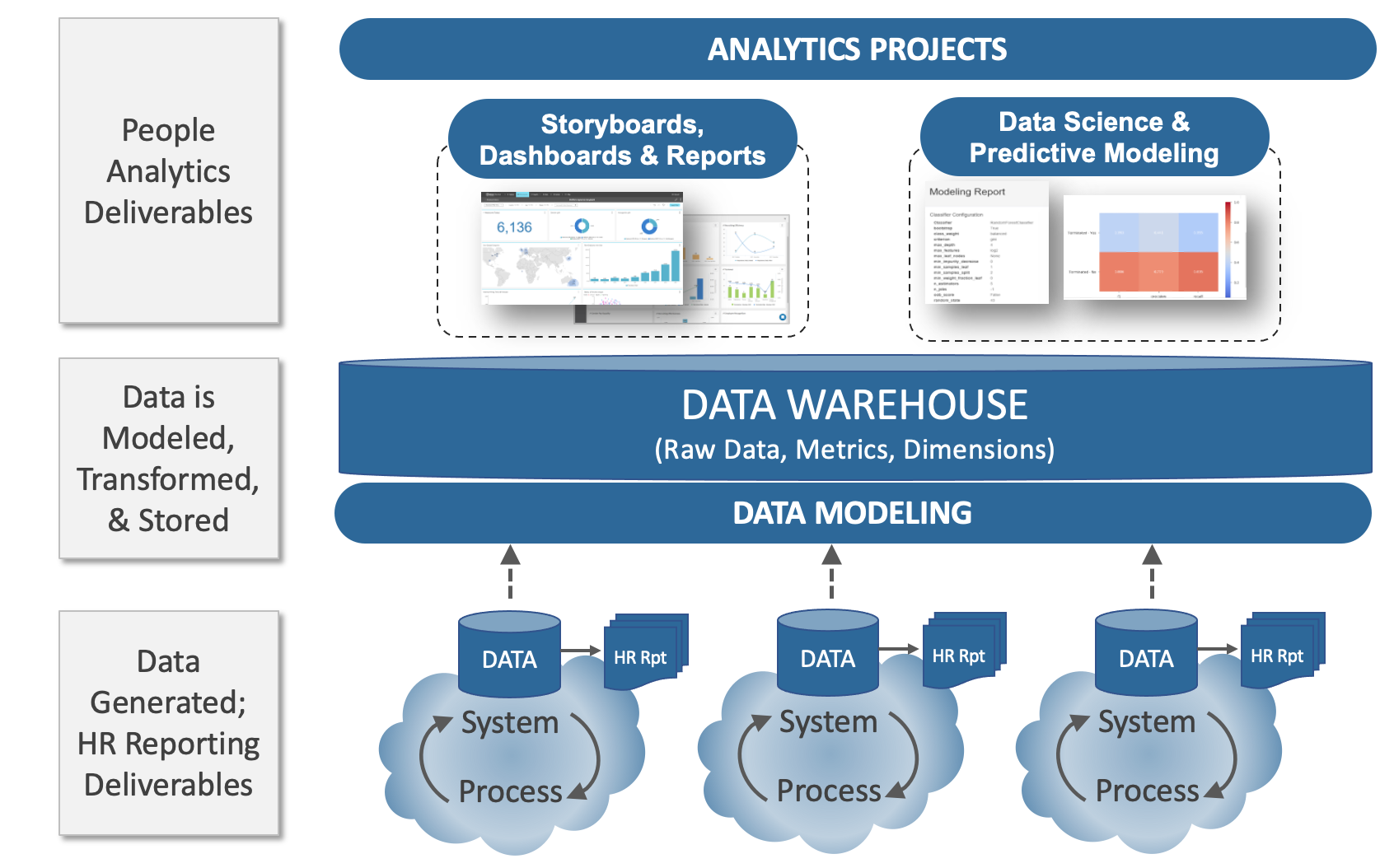
Reporting and Analytics

Accurate and timely HR reports are the lifeblood of effective HR management. They provide crucial insights into workforce trends, allowing organizations to make data-driven decisions that optimize performance, improve employee experience, and ultimately, boost the bottom line. Without robust reporting capabilities, HR departments are operating in the dark, unable to identify critical areas for improvement or measure the success of their initiatives.
HRIS systems offer powerful tools for generating these reports, transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. The ability to quickly access and analyze key metrics empowers HR professionals to proactively address challenges and capitalize on opportunities, ensuring the organization remains competitive and agile in today’s dynamic landscape.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in HRIS
Tracking the right KPIs is paramount for understanding the health and performance of your workforce. These metrics provide a quantifiable measure of HR initiatives and their impact on the organization’s overall goals.
Examples of commonly tracked KPIs include employee turnover rate, employee satisfaction scores, time-to-hire, cost-per-hire, training effectiveness, and diversity and inclusion metrics. By monitoring these KPIs regularly, HR can identify trends, pinpoint areas of weakness, and implement targeted interventions.
Employee Turnover Analysis Report
Understanding employee turnover is crucial for reducing costs associated with recruitment and training, improving employee morale, and maintaining institutional knowledge. Analyzing turnover helps identify underlying issues and implement retention strategies.
The following sample report demonstrates an analysis of employee turnover, focusing on department-specific trends. Visualizations, such as bar charts, can highlight key differences in turnover rates across various departments.
| Department | Number of Employees | Number of Departures | Turnover Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | 50 | 5 | 10% |
| Marketing | 30 | 3 | 10% |
| Engineering | 70 | 7 | 10% |
| Human Resources | 10 | 1 | 10% |
HR Metrics Dashboard
A well-designed HR metrics dashboard provides a comprehensive overview of key performance indicators, enabling quick identification of trends and potential problems. Different chart types are selected to best represent the data being presented.
For example, a dashboard might utilize bar charts to compare employee satisfaction scores across different departments, line charts to track employee turnover rates over time, and pie charts to illustrate the distribution of employees across various demographic categories. Key metrics, such as average tenure and cost-per-hire, can be displayed as simple numerical values for quick reference. The selection of charts and graphs should prioritize clarity and ease of interpretation, ensuring that critical insights are easily accessible to all stakeholders.
Data Visualization and Interpretation
Unlocking the power of your HRIS data isn’t just about collecting it; it’s about understanding what it tells you. Effective data visualization transforms raw numbers into actionable insights, guiding strategic HR decisions and improving overall organizational performance. By presenting data in clear, concise, and compelling ways, you can influence stakeholders and drive positive change.Effective methods for visualizing HR data are crucial for translating complex information into easily digestible formats.
Different visualization techniques cater to different types of data and audiences, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of HR trends and patterns. This ultimately helps in making better-informed decisions, leading to more effective HR strategies.
Choosing the Right Visualization Method
The selection of visualization methods depends heavily on the type of data and the message you want to convey. For instance, a bar chart is ideal for comparing different categories (e.g., employee turnover rates across departments), while a line chart effectively illustrates trends over time (e.g., employee satisfaction scores over the past year). Pie charts are useful for showing proportions (e.g., the percentage of employees in different age groups), and scatter plots can reveal correlations between two variables (e.g., employee performance and training hours).
Best practices for HRIS data management and reporting emphasize accuracy and accessibility. For remote teams, leveraging a cloud-based system significantly improves these aspects; check out the benefits of cloud-based HRIS systems for remote teams to see how. Ultimately, efficient data management, regardless of location, ensures better decision-making and streamlined HR processes.
Heatmaps are particularly useful for displaying large datasets, highlighting areas of high or low values. Choosing the right chart type ensures your data is presented clearly and effectively.
Examples of Effective Visualizations
Imagine a bar chart showcasing employee turnover rates by department. A taller bar for a specific department immediately highlights a potential issue requiring attention. Another example could be a line graph showing employee satisfaction scores over time. A downward trend clearly indicates a need for intervention and improvement strategies. A heatmap could visually represent employee skills across different teams, instantly identifying skill gaps and potential training needs.
These visualizations, when properly designed and contextualized, become powerful tools for communication and decision-making.
Interpreting HR Data Trends for Improvement, Best practices for HRIS data management and reporting
Analyzing visualized data goes beyond simply observing the charts; it’s about interpreting the trends and patterns to identify areas for improvement. For example, a consistent downward trend in employee engagement scores over several quarters might suggest a need to review company culture, leadership styles, or employee recognition programs. Similarly, high employee turnover in a specific department could indicate issues with management, workload, or compensation.
By connecting the visual representation of data to potential underlying causes, HR professionals can proactively address challenges and improve HR processes.
Presenting HR Data Insights
Presenting HR data insights effectively requires a clear narrative. Start by defining the key message or story you want to convey. Then, select the appropriate visualization method(s) to support your narrative. For example, to showcase the impact of a new training program, you might use a before-and-after bar chart comparing employee performance metrics. Ensure the presentation is concise, focusing on the most important findings and their implications.
Use clear and simple language, avoiding jargon, and tailor the presentation to the audience’s level of understanding. Remember, the goal is to communicate actionable insights, not to overwhelm the audience with complex data.
Compliance and Auditing
Maintaining a compliant and auditable HRIS system is crucial not only for legal reasons but also for building trust with employees and stakeholders. Robust data management practices directly impact your organization’s ability to demonstrate adherence to relevant regulations and maintain data integrity. Failing to do so can lead to hefty fines, reputational damage, and loss of employee confidence.Effective HRIS data management aligns with legal and regulatory requirements such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
These regulations demand stringent data protection measures, including consent management, data minimization, and the right to data access and erasure. Compliance necessitates a proactive approach, embedding data governance principles throughout the entire HRIS lifecycle.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Organizations must ensure their HRIS data management practices comply with all applicable laws and regulations regarding data privacy and security. This includes implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments. For example, GDPR requires organizations to document their data processing activities, including the legal basis for processing, the categories of data processed, and the recipients of the data.
Similarly, CCPA mandates that organizations provide consumers with the ability to access, correct, and delete their personal information. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties. A documented data protection impact assessment (DPIA) for high-risk processing activities is also often a legal requirement.
HRIS Data Audit Procedures
Regular audits are essential to verify the effectiveness of HRIS data management controls and ensure ongoing compliance. These audits should encompass data accuracy, completeness, security, and adherence to relevant regulations. A comprehensive audit plan should be developed, outlining the scope, methodology, and timeline of the audit. The audit team should possess the necessary expertise in data governance, security, and relevant regulations.
The audit should involve reviewing policies and procedures, examining system configurations, and testing controls. Discrepancies or weaknesses identified during the audit should be documented and addressed promptly with corrective action plans. Regular audits provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of data management practices and highlight areas for improvement.
Documentation for Data Privacy Compliance
Maintaining comprehensive documentation is critical for demonstrating compliance with data privacy regulations. This documentation should include:
- Data processing inventory: A detailed list of all personal data processed by the HRIS system, including the purpose of processing, the legal basis, and the categories of data subjects.
- Data security policy: A document outlining the organization’s policies and procedures for protecting personal data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
- Data breach response plan: A plan outlining the steps to be taken in the event of a data breach, including notification procedures and remediation measures.
- Records of consent: Documentation of consent obtained from data subjects for the processing of their personal data.
- Data subject access requests (DSAR) logs: A record of all DSARs received, the actions taken, and the outcomes.
This documentation serves as evidence of compliance during audits or investigations.
HRIS Data Audit Checklist
A thorough HRIS data audit should include the following:
- Review of data governance policies and procedures.
- Assessment of data security controls (access controls, encryption, etc.).
- Verification of data accuracy and completeness.
- Examination of data retention policies and procedures.
- Review of data backup and recovery procedures.
- Assessment of compliance with relevant regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.).
- Review of data subject access request (DSAR) processes.
- Documentation review.
- Identification and remediation of any identified vulnerabilities or weaknesses.
This checklist ensures a comprehensive and systematic approach to auditing HRIS data, helping to identify and address potential risks and compliance issues.
Data Backup and Recovery

Protecting your HRIS data is paramount. A robust backup and recovery strategy is not just a good idea—it’s a necessity to ensure business continuity and prevent irreversible data loss. This section Artikels various strategies and best practices to safeguard your valuable HR information.Data backup involves creating copies of your HRIS data to a separate location. This ensures that even if the primary system fails, you can restore your data and resume operations.
Different backup methods offer varying levels of protection and resource consumption.
Backup Strategies for HRIS Data
Choosing the right backup strategy depends on factors like data volume, recovery time objectives (RTO), and recovery point objectives (RPO). A balanced approach often combines different methods.
- Full Backup: A complete copy of all HRIS data. This is time-consuming but provides a complete recovery point. Think of it as taking a snapshot of your entire system at a specific moment.
- Incremental Backup: Only backs up data that has changed since the last full or incremental backup. This is faster and more efficient than full backups, but recovery involves restoring the full backup and then applying all subsequent incremental backups.
- Differential Backup: Backs up only the data that has changed since the last full backup. This is faster than a full backup and offers a faster recovery time than incremental backups, but uses more storage space than incremental backups.
Disaster Recovery Methods for HRIS Systems
Disaster recovery (DR) plans Artikel procedures for restoring HRIS functionality after a disruptive event. Several methods exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
- On-site Backup: Keeping backups in a physically separate location within the same building or campus. This is cost-effective but vulnerable to the same local disasters (fire, flood).
- Off-site Backup: Storing backups in a geographically separate location, such as a cloud storage provider or a secure off-site data center. This offers better protection against localized disasters but might have higher costs and longer recovery times.
- Cloud-Based DR: Utilizing cloud services for both backup and recovery. This offers scalability, flexibility, and often automatic backups, but requires careful consideration of security and compliance aspects.
Designing a Disaster Recovery Plan for an HRIS System
A comprehensive DR plan should cover various scenarios and include detailed procedures.
A well-structured plan will include:
- Data Recovery Procedures: Step-by-step instructions for restoring data from backups, including specifying the backup method, restoration tools, and verification steps.
- Business Continuity Strategies: Plans for maintaining critical HR functions during downtime, such as utilizing alternative communication channels or temporary manual processes.
- Communication Plan: A clear communication plan to inform employees, management, and stakeholders about the incident and recovery progress.
- Testing and Maintenance: Regularly scheduled tests and updates to the plan to ensure its effectiveness and relevance.
Testing the Effectiveness of the Disaster Recovery Plan
Regular testing is crucial to validate the DR plan’s effectiveness.
Testing should include:
- Tabletop Exercises: Simulated disaster scenarios discussed by the recovery team to identify potential weaknesses and refine procedures.
- Partial System Restoration: Restoring a portion of the HRIS system from backups to assess the restoration process and identify potential issues.
- Full System Restoration: A complete restoration of the HRIS system from backups, simulating a complete system failure. This is the most comprehensive but also the most resource-intensive test.