How to measure the ROI of an HRIS system implementation? That’s the million-dollar question every HR professional grapples with. Investing in a new HR Information System is a big deal, and proving its worth requires a strategic approach. This isn’t just about crunching numbers; it’s about demonstrating the tangible impact on efficiency, employee engagement, and ultimately, the bottom line.
We’ll delve into the key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter, show you how to track them, and ultimately paint a clear picture of your HRIS’s return on investment.
From quantifying cost savings through automation to assessing improvements in employee satisfaction and talent acquisition, we’ll equip you with the tools and insights you need to build a compelling ROI case. Think of it as your ultimate guide to justifying that HRIS investment and showcasing its transformative power within your organization.
Defining Measurable HRIS Outcomes: How To Measure The ROI Of An HRIS System Implementation?
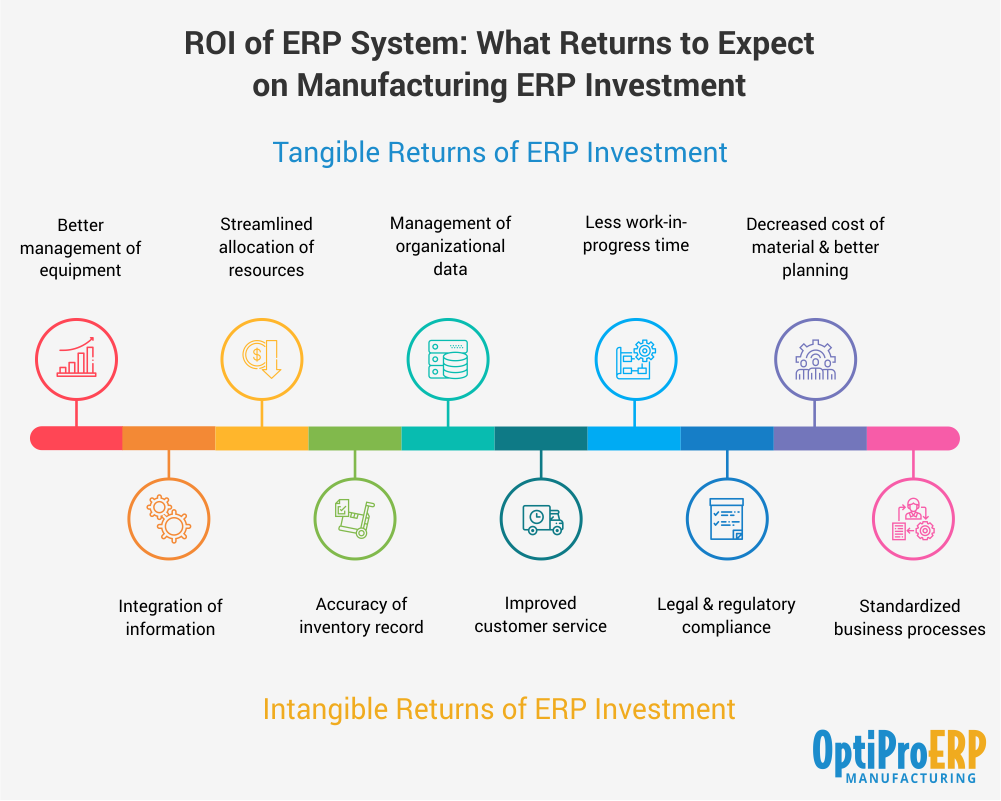
Successfully measuring the return on investment (ROI) of an HRIS implementation hinges on clearly defining and tracking the right metrics. This isn’t about simply tracking data; it’s about identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) that directly reflect the value the HRIS brings to the organization. By focusing on measurable outcomes, you can demonstrate the tangible benefits of your investment and justify future HR tech upgrades.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for HRIS Success
Establishing a robust set of KPIs is crucial for tracking the effectiveness of your HRIS implementation. These KPIs should be carefully selected to align with your organization’s strategic goals and provide a clear picture of the system’s impact. The following table Artikels some essential KPIs, their measurement methods, data sources, and potential targets. Remember, these targets are illustrative and should be tailored to your specific context and organizational goals.
| KPI | Measurement Method | Data Source | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time-to-hire | Calculate the average time taken to fill open positions. | Applicant Tracking System (ATS) within the HRIS | Reduce time-to-hire by 15% within six months. |
| Employee Turnover Rate | Calculate the percentage of employees leaving the company within a specific period. | HRIS employee database | Reduce employee turnover by 10% annually. |
| Employee Satisfaction | Conduct regular employee surveys and analyze feedback related to HR processes. | HRIS employee surveys module, feedback forms | Achieve an average employee satisfaction score of 4.0 out of 5.0. |
| Recruitment Cost per Hire | Divide total recruitment costs by the number of hires. | HRIS recruitment module, finance department data | Reduce recruitment cost per hire by 10%. |
| Training and Development Costs | Track the cost of training programs delivered through the HRIS. | HRIS learning management system (LMS) module, finance department data | Reduce training costs by 5% while increasing employee participation by 10%. |
| Payroll Processing Time | Measure the time taken to process payroll from start to finish. | HRIS payroll module | Reduce payroll processing time by 20%. |
| Employee Self-Service Usage Rate | Track the percentage of employees using self-service features. | HRIS system logs | Increase self-service usage rate to 80%. |
Establishing Baseline Metrics
Before implementing the HRIS, it’s vital to establish baseline metrics for each chosen KPI. This provides a benchmark against which to measure the system’s impact after implementation. This involves gathering historical data on the chosen KPIs using existing systems (manual or automated). For example, if you’re tracking time-to-hire, you’d collect data on the average time taken to fill open positions over the past year.
Analyzing this data provides a clear picture of the current state and allows for a more accurate assessment of the HRIS’s effectiveness.
Aligning HRIS KPIs with Business Objectives
The KPIs you choose should directly support your organization’s overall business objectives. For example, if a key business objective is to improve employee retention, then KPIs like employee satisfaction and employee turnover rate become critical. By aligning HRIS KPIs with broader business goals, you can demonstrate the system’s contribution to the company’s bottom line and justify the investment in terms of strategic value.
For instance, a reduction in employee turnover directly translates to reduced recruitment costs and improved productivity, which are directly linked to profitability.
Quantifying Cost Savings and Efficiencies
Implementing an HRIS system isn’t just about upgrading technology; it’s about strategically optimizing HR processes for maximum efficiency and cost savings. By automating tasks and streamlining workflows, a well-integrated HRIS can significantly reduce operational expenses and free up valuable employee time. This section delves into specific ways to quantify these cost reductions and improvements in efficiency, allowing you to build a compelling case for your HRIS investment.
The key to demonstrating the financial benefits of your HRIS lies in identifying and quantifying the areas where it delivers cost savings and boosts efficiency. This involves a careful assessment of your pre- and post-implementation processes, focusing on areas like payroll processing, recruitment, onboarding, and employee self-service. By meticulously tracking these metrics, you can build a robust ROI calculation that showcases the true value of your HRIS.
Examples of Cost Reduction Through Automation
Automation is a cornerstone of HRIS efficiency. Several areas experience significant cost reductions after implementing an HRIS system capable of automation. These savings stem from reduced manual effort, fewer errors, and optimized resource allocation.
- Payroll Processing: Automated payroll calculations and direct deposit eliminate manual checks, reducing labor costs associated with data entry, reconciliation, and distribution. Consider a scenario where manual payroll processing took 20 hours per pay period at a cost of $50/hour. With automation, this could be reduced to 5 hours, saving $750 per pay period.
- Recruitment: Automated applicant tracking systems streamline the screening and selection process, reducing time-to-hire and associated recruiter costs. Imagine a reduction in time-to-hire from 4 weeks to 2 weeks, saving on recruiter time and associated advertising expenses.
- Onboarding: Automated onboarding workflows eliminate manual paperwork, expedite the process, and improve the new hire experience. This reduces the administrative burden on HR staff and potentially speeds up employee productivity.
- Benefits Administration: Automated enrollment and management of employee benefits simplifies the process for both employees and HR, minimizing errors and reducing administrative overhead. For example, automated benefits enrollment could reduce the number of manual corrections needed by 50%, saving significant time and resources.
Calculating ROI Related to Time Saved
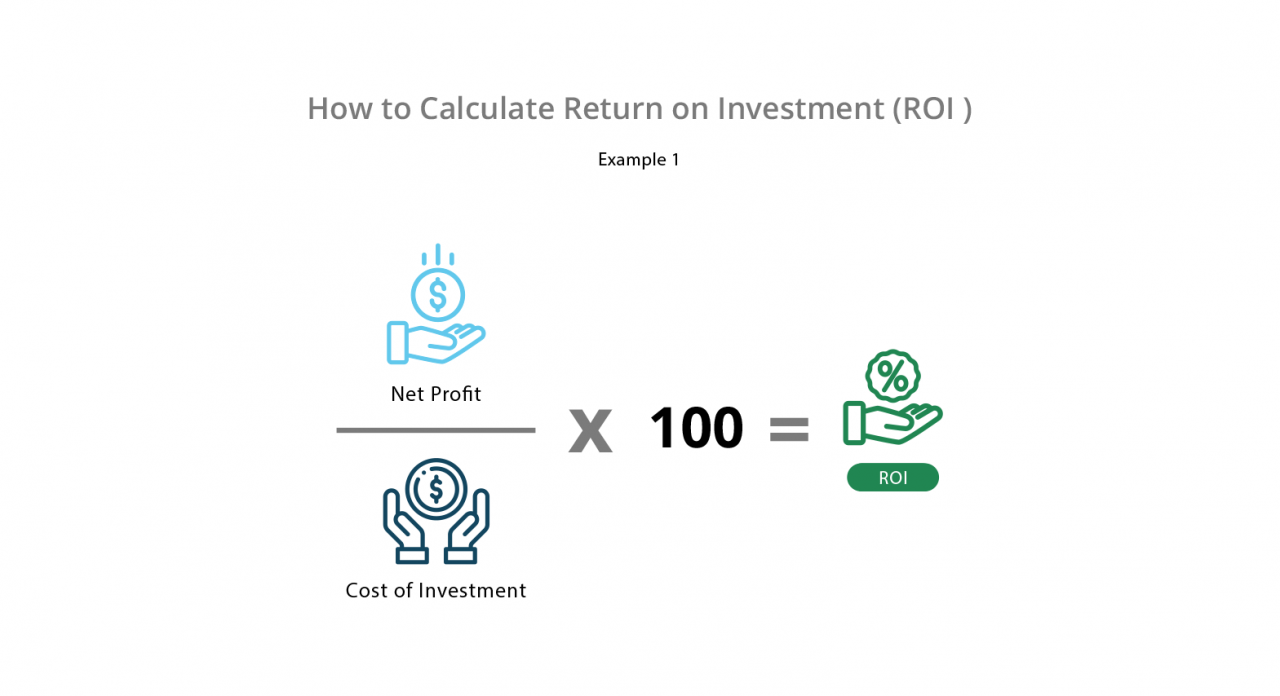
Quantifying the return on investment related to time saved requires a systematic approach. It involves calculating the value of the time saved on HR tasks and comparing it to the cost of the HRIS implementation.
To calculate this, first determine the time saved per task or process. Then, assign a value to that time based on the hourly rate of the employees performing those tasks. Finally, multiply the time saved by the hourly rate to get the total cost savings.
The formula for calculating ROI based on time saved is: ROI = (Total Time Saved x Hourly Rate – HRIS Implementation Cost) / HRIS Implementation Cost
Calculating the ROI of your new HRIS? Don’t forget that a smooth implementation is key! This often hinges on choosing the right vendor, so thoroughly research potential partners; check out this guide on selecting HRIS system vendors with excellent customer support to avoid costly post-implementation headaches. Ultimately, strong vendor support directly impacts your HRIS’s overall effectiveness and return on investment.
For example, if automating a process saves 10 hours per week for an employee earning $50/hour, the weekly savings are $500. Annual savings would be $26,000 (assuming 52 weeks). This figure can then be compared against the total cost of the HRIS implementation to determine the ROI.
Quantifying the Impact of Reduced Administrative Errors
Administrative errors can be costly, leading to delays, rework, and potential legal issues. An HRIS system with robust data validation and workflow automation significantly reduces these errors. Quantifying the impact requires estimating the cost of past errors and comparing it to the error rate after HRIS implementation.
To calculate this, estimate the cost associated with each type of error (e.g., incorrect payroll payments, delayed onboarding, inaccurate performance reviews). Then, multiply this cost by the number of errors avoided due to the HRIS. For example, if the HRIS reduces payroll errors by 50%, and each error costs $100 to rectify, the annual savings would be significant, depending on the volume of payroll transactions.
Assessing Employee Engagement and Productivity
Measuring the impact of an HRIS system goes beyond cost savings; it’s crucial to understand its effect on employee engagement and productivity. A happy, productive workforce is the ultimate ROI, and a well-implemented HRIS can significantly contribute to this. By tracking key metrics and gathering employee feedback, you can quantify the positive influence of your new system.
The post-implementation phase is critical for assessing the system’s impact on employee experience and overall performance. This involves a multi-pronged approach that combines quantitative data with qualitative feedback to paint a complete picture.
Employee Satisfaction and Engagement Measurement
Post-implementation surveys and feedback mechanisms are vital for gauging employee satisfaction and engagement. These tools provide valuable insights into how the HRIS is affecting the employee experience, identifying areas of strength and areas needing improvement. A structured approach ensures you collect relevant data and accurately interpret the results.
- Pre- and Post-Implementation Surveys: Conduct employee satisfaction surveys before and after HRIS implementation to compare changes in key areas like ease of access to information, self-service capabilities, and overall HR support.
- Regular Pulse Surveys: Implement short, regular pulse surveys to monitor ongoing employee sentiment towards the HRIS and identify emerging issues or concerns promptly. These can be deployed weekly or monthly, depending on your needs.
- Focus Groups: Organize focus groups with representatives from different departments to gather in-depth feedback on specific aspects of the HRIS. This qualitative data can enrich the quantitative data gathered through surveys.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish multiple feedback channels, such as suggestion boxes, online feedback forms, and regular employee meetings, to encourage open communication and continuous improvement.
Productivity Metrics
Several key metrics can reflect improvements in employee productivity following HRIS implementation. Focusing on these metrics provides a clear indication of the system’s impact on the bottom line.
- Time-to-Hire: A well-designed HRIS can streamline the recruitment process, reducing the time it takes to fill open positions. Track this metric to see if your time-to-hire has improved post-implementation.
- Employee Turnover Rate: Higher employee engagement often correlates with lower turnover. Monitor your turnover rate to see if the HRIS has contributed to improved employee retention.
- Employee Absenteeism Rate: A user-friendly and efficient HRIS can simplify processes like leave requests, potentially reducing absenteeism. Track absenteeism rates to assess this potential impact.
- Training Time: Measure the time it takes to train employees on new systems and processes. An effective HRIS should minimize training time and accelerate onboarding.
Collecting and Analyzing Employee Feedback on HRIS Usability
Gathering and analyzing employee feedback on the HRIS’s user-friendliness and effectiveness is crucial for continuous improvement. A structured approach ensures you collect meaningful data and act upon it.
- Usability Testing: Conduct usability testing sessions with a representative sample of employees to identify areas where the system is difficult to use or understand. This might involve observing employees using the system and asking them to complete specific tasks.
- System Feedback Forms: Integrate feedback forms directly into the HRIS, allowing employees to easily report bugs, suggest improvements, or provide general feedback on their experience.
- Regular System Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of employee feedback to identify trends and patterns. This will help prioritize improvements and ensure the HRIS remains user-friendly and effective.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the collected feedback data to identify common themes and areas for improvement. Use this data to inform decisions about system updates and enhancements.
Measuring Talent Acquisition and Management Improvements

Implementing an HRIS system often promises streamlined recruitment processes and improved talent management. Measuring the impact on these key areas is crucial for demonstrating the system’s ROI. By analyzing key metrics before and after implementation, you can quantify the tangible benefits of your investment.
Time-to-Fill for Open Positions
Tracking the time-to-fill metric provides a clear indication of the efficiency gains achieved through HRIS implementation. A shorter time-to-fill translates to faster onboarding of new employees and reduced costs associated with prolonged vacancies. The following table compares this metric before and after the HRIS system was implemented. Note that these are example figures and will vary significantly depending on the industry, company size, and specific roles.
| Before Implementation | After Implementation |
|---|---|
| 45 days | 30 days |
| 60 days | 40 days |
| 35 days | 25 days |
| 50 days | 35 days |
| Average: 47.5 days | Average: 32.5 days |
Impact of HRIS on Quality of Hire
Beyond speed, the HRIS system should also improve the quality of hires. This can be measured by tracking employee retention rates, performance reviews, and employee satisfaction surveys among those hired after the HRIS implementation. A robust HRIS often allows for more effective screening of candidates, leading to better matches between job requirements and candidate skills. For example, an integrated applicant tracking system can automate the process of screening resumes, reducing the risk of overlooking qualified candidates.
Similarly, improved candidate communication features can lead to a more positive candidate experience and increased acceptance rates of job offers. This ultimately leads to a higher quality of hire and reduced turnover.
Cost Per Hire
Cost per hire (CPH) is a critical metric for evaluating the financial impact of recruitment efforts. It’s calculated by dividing the total cost of hiring by the number of hires made. A reduction in CPH demonstrates the financial benefits of HRIS implementation. The following illustrates a hypothetical example of CPH before and after HRIS implementation. Note that these figures are for illustrative purposes and actual costs will vary based on several factors including location, industry, and seniority of roles.
Cost Per Hire (CPH) = Total Cost of Hiring / Number of Hires
For instance, if the total cost of hiring for 10 positions was $50,000 before implementation, the CPH would be $5,000. After implementing the HRIS, if the total cost for hiring 12 positions dropped to $48,000, the CPH would be approximately $4,000, representing a 20% reduction. This decrease could be attributed to automation of tasks, improved candidate sourcing, and reduced time spent on administrative processes.
Calculating the ROI of an HRIS implementation requires a multifaceted approach. Key metrics include reduced administrative costs and improved employee satisfaction. A significant part of this return comes from streamlined talent processes; understanding how these improvements impact your bottom line is crucial. To see how an HRIS boosts efficiency in this area, check out this insightful article: How does an HRIS system enhance talent acquisition and management?
Ultimately, measuring the ROI boils down to comparing pre- and post-implementation data across key HR functions.
Analyzing Training and Development Effectiveness
An HRIS system’s impact extends beyond basic HR functions; it significantly influences the effectiveness of training and development initiatives. By streamlining processes and providing data-driven insights, a well-implemented HRIS allows HR professionals to design, deliver, and evaluate training programs with greater precision and efficiency, ultimately boosting employee skills and organizational performance. This section explores how to measure the return on investment (ROI) specifically related to training and development facilitated by your HRIS.The HRIS system facilitates training and development programs in several key ways, directly impacting employee skill enhancement and organizational growth.
These improvements contribute significantly to the overall ROI of the system.
HRIS System Facilitation of Training and Development
The integration of training and development programs within an HRIS system offers numerous advantages. This streamlined approach ensures efficient program delivery and allows for comprehensive tracking of employee progress.
- Automated Course Registration and Enrollment: Employees can easily register for courses through a self-service portal, eliminating manual processes and reducing administrative overhead.
- Personalized Learning Paths: The HRIS can recommend training based on employee roles, skills gaps, and performance data, creating personalized learning journeys that maximize impact.
- Centralized Content Repository: All training materials, including videos, presentations, and documents, are stored in a single, accessible location, improving organization and reducing search time.
- Integrated Assessment and Feedback Tools: The HRIS can facilitate pre- and post-training assessments, enabling objective measurement of learning outcomes and providing valuable feedback to both employees and trainers.
- Tracking of Training Completion and Certification: The system automatically tracks employee participation, completion rates, and certifications earned, providing a clear picture of program effectiveness.
Measuring Training Program Effectiveness
Measuring the effectiveness of training delivered through the HRIS system requires a multi-faceted approach. This involves tracking not only completion rates but also the impact on employee performance, productivity, and overall organizational goals. The key is to establish clear metrics beforehand and consistently monitor them.Effective measurement goes beyond simply tracking completion rates. It requires assessing the impact of training on key performance indicators (KPIs).
For instance, a sales training program’s effectiveness could be measured by tracking an increase in sales revenue per employee post-training. Similarly, a customer service training program’s success could be evaluated based on improved customer satisfaction scores. This data-driven approach provides concrete evidence of the training’s ROI.
Tracking Employee Participation and Completion Rates
Tracking employee participation and completion rates is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of training programs delivered through the HRIS. The HRIS itself provides the necessary tools for this.The HRIS system automatically records employee registration, course enrollment, progress, and completion. This data can be easily accessed and analyzed to generate reports on participation rates, completion rates, and time to completion.
These metrics provide insights into employee engagement with the training programs and help identify any areas requiring improvement. For example, low completion rates for a particular course might indicate the need for adjustments to the course content or delivery method. Furthermore, analyzing completion rates across different departments or employee groups can highlight potential disparities in training needs or access.
By setting clear targets for participation and completion rates, organizations can track progress and measure the success of their training initiatives. Regular monitoring of these metrics allows for timely adjustments to ensure the training programs remain relevant and effective.
Visualizing ROI Data

Data visualization is crucial for effectively communicating the return on investment (ROI) of your HRIS system implementation. Transforming complex data into easily digestible visuals allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the impact and justify continued investment. Clear, concise visualizations make the ROI story compelling and understandable, even for those without a deep understanding of HR metrics.
Line Graph Showing Cost Savings Over Time, How to measure the ROI of an HRIS system implementation?
A line graph provides a clear picture of cost savings achieved through the HRIS system implementation over a defined period. The horizontal axis (x-axis) represents time, typically in months or years, starting from the pre-implementation phase and extending to the current period. The vertical axis (y-axis) represents the total cost savings in monetary units (e.g., dollars, euros). Each data point on the graph represents the cumulative cost savings at a specific point in time.
For example, a data point at month six might show a cumulative savings of $15,000, while the data point at month twelve might show $30,000, demonstrating a clear upward trend. A trendline can be added to highlight the overall growth in cost savings. This visual clearly showcases the increasing financial benefits of the HRIS system over time.
Bar Chart Comparing Key Metrics Before and After Implementation
A bar chart effectively compares key HR metrics before and after the HRIS implementation. Two sets of bars are used, one representing the pre-implementation values and the other representing the post-implementation values. The x-axis displays the key metrics being compared (e.g., time-to-hire, employee turnover rate, training completion rate). The y-axis represents the metric’s value (e.g., number of days, percentage, number of employees).
For instance, a bar representing “time-to-hire” before implementation might show an average of 45 days, while the corresponding post-implementation bar might show a reduced average of 30 days, visually highlighting the improvement. This allows for a direct comparison and immediate understanding of the positive impact of the HRIS. Using different colors for pre- and post-implementation bars enhances readability.
Visual Representation Showing the Correlation Between HRIS Usage and Improved KPIs
A scatter plot can effectively illustrate the correlation between HRIS usage and improved key performance indicators (KPIs). The x-axis represents the level of HRIS usage (e.g., number of users, frequency of logins, modules utilized), and the y-axis represents the value of a specific KPI (e.g., employee satisfaction score, employee retention rate). Each data point represents a specific period or employee group, plotting their HRIS usage against their corresponding KPI value.
A trendline can be added to visually represent the correlation. For example, a positive correlation would show that as HRIS usage increases, the KPI value also tends to increase, visually demonstrating the positive impact of the system on key business outcomes. This visual effectively supports the claim that increased HRIS usage leads to improved organizational performance.